Understanding the Difference Between Active and Passive Voice
Table of Contents
Introduction
Active and Passive Voice
When it comes to writing, the use of active and passive voice plays a crucial role in determining the clarity and impact of a sentence. Understanding the difference between the two can greatly enhance the quality of your writing. Let’s explore the concepts of active and passive voice and learn how to use them effectively.
Analogy of Definition
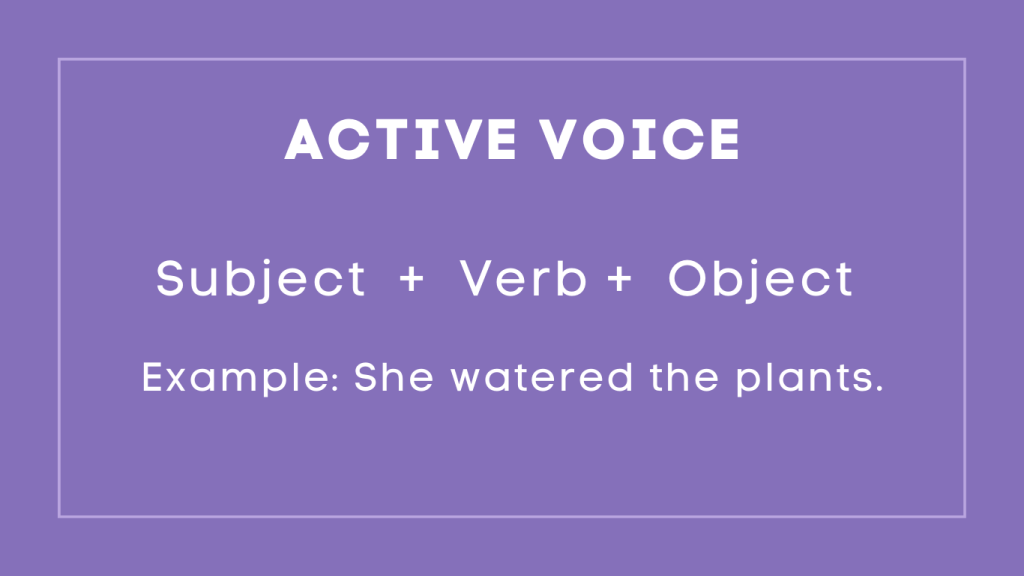
Active Voice
Active voice is a grammatical structure in which the subject of a sentence performs the action denoted by the verb. In active voice, the subject acts upon the object, resulting in clearer and more direct sentences. Writers often prefer using active voice because it emphasizes the doer of the action and enhances the readability of their writing.
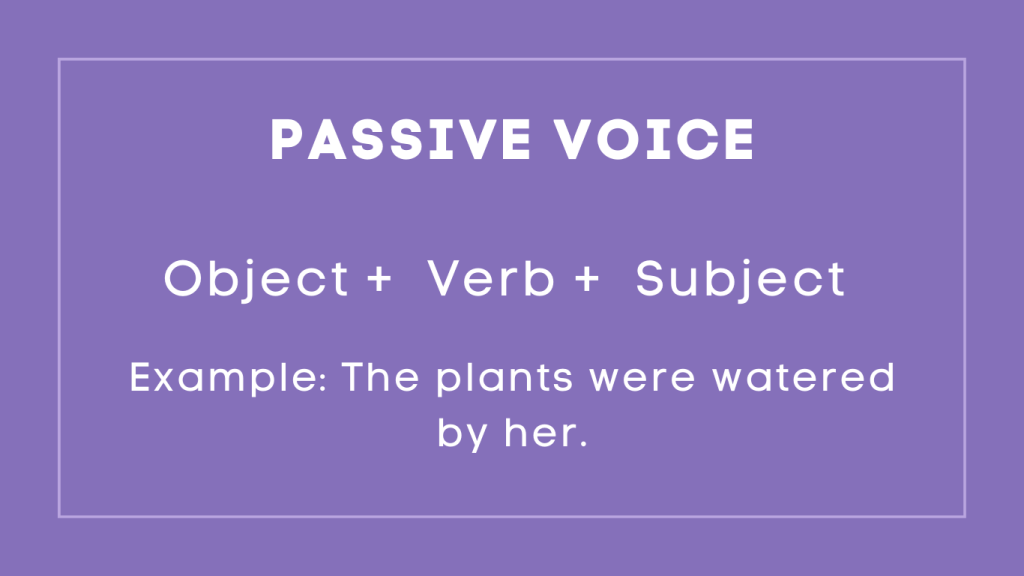
Passive Voice
In contrast, passive voice is a grammatical structure in which the subject of the sentence is acted upon by the verb. This construction is often used when the doer of the action is unknown or when the focus is on the receiver of the action rather than the doer. Additionally, passive voice can be employed to create a sense of formality or to shift emphasis within a sentence. Understanding the distinction between the two is essential for effective communication.
Method
Changing Passive Voice to Active Voice
To change a sentence from passive voice to active voice, you need to identify the subject performing the action and make it the focus of the sentence. You should also rephrase the sentence to ensure that the subject is the doer of the action. Changing from passive voice to active voice involves reordering the sentence so that the subject performing the action becomes the subject of the active sentence. You also need to adjust the verb to its active form and, if necessary, identify the receiver of the action as the object.
Example:
Passive voice: “The book was read by Sarah.”
Active voice: “Sarah read the book.”
In the passive voice, “the book” is the subject receiving the action, and “was read” is the verb indicating the action done to the book by Sarah. In the active voice, “Sarah” becomes the subject performing the action, “read” is the active verb, and “the book” becomes the object receiving the action.
Changing Active Voice to Passive Voice
Conversely, to change a sentence from active voice to passive voice, you need to restructure the sentence so that the object of the action becomes the subject. The verb should be changed to a form of “to be” followed by the past participle of the main verb. The verb is changed to a form of “be” (such as “is,” “was,” “are,” etc.), followed by the past participle of the main verb. Finally, if needed, the doer of the action (the agent) can be included using the preposition “by.”
Example:
Active voice: “The cat chased the mouse.”
Passive voice: “The mouse was chased by the cat.”
In the active voice, the cat is the subject performing the action (chasing), while the mouse is the object receiving the action. In the passive voice, the focus shifts to the mouse, which becomes the subject, and the verb changes to “was chased,” with “by the cat” indicating the doer of the action (the agent).
Active Voice vs Passive Voice
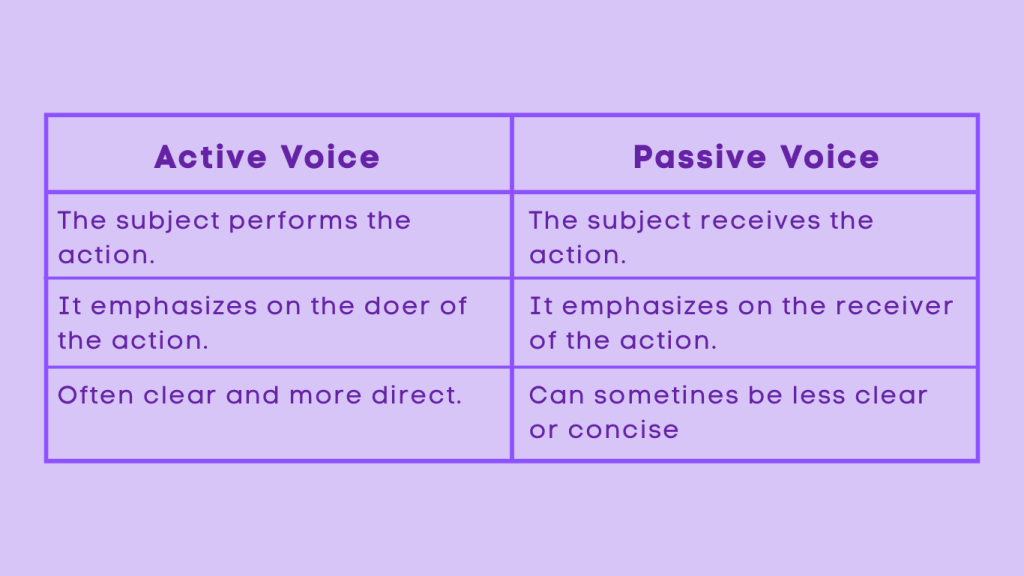
Examples
Changing Passive Voice to Active Voice
Passive Voice: The cake was baked by Mary.
Active Voice: Mary baked the cake.
Changing Active Voice to Passive Voice
Active Voice: The dog chased the cat.
Passive Voice: The cat was chased by the dog.
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Changing Passive Voice to Active Voice
Tip: To change passive voice to active voice, identify the subject performing the action and make it the focus of the sentence.
Example: Passive Voice – The cake was baked by Mary. Active Voice – Mary baked the cake.
2. Changing Active Voice to Passive Voice
Tip: When changing active voice to passive voice, restructure the sentence so that the object of the action becomes the subject.
Example: Active Voice – The dog chased the cat. Passive Voice – The cat was chased by the dog.
3. Identifying Active and Passive Voice
Tip: Active voice emphasizes the doer of the action, while passive voice emphasizes the receiver of the action.
Example: Active Voice – The chef prepared the meal. Passive Voice – The meal was prepared by the chef.
4. Focus on the Subject
Tip: In active voice, the subject is the doer of the action, while in passive voice, the subject is the receiver of the action.
Example: Active Voice – The students completed the project. Passive Voice – The project was completed by the students.
5. Verb Forms in Active and Passive Voice
Tip: Pay attention to the verb forms when changing between active and passive voice to ensure grammatical accuracy.
Example: Active Voice – The team won the game. Passive Voice – The game was won by the team.
Real life application
Story: “The Writing Challenge”
In a writing competition, participants were given a challenge to write a story using both active and passive voice to demonstrate their understanding of the concept. Let’s explore how the participants utilized active and passive voice in their stories.
Participant 1: Active Voice Emphasis
One participant focused on using active voice to create a sense of immediacy and directness in the story. By emphasizing the actions of the characters, the narrative felt dynamic and engaging, drawing the readers into the plot.
Participant 2: Passive Voice Elegance
Another participant chose to incorporate passive voice to convey a sense of mystery and elegance in the story. By shifting the focus to the objects and recipients of the actions, the narrative took on a more reflective and contemplative tone, adding depth to the storytelling.
Participant 3: Voice Harmony
A third participant skillfully blended active and passive voice to create a harmonious narrative that balanced the impact of the actions with the significance of the recipients. This approach added complexity and nuance to the storytelling, captivating the readers with its rich texture.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends






