Compound Sentences – Meaning and Examples
Table of Contents
Introduction
Compound Sentences
In the realm of grammar and language, compound sentences play a crucial role in conveying complex ideas and connecting related thoughts. Understanding the structure and usage of compound sentences is essential for effective communication and writing. Let’s delve into the world of compound sentences and explore their various forms and applications.
Analogy of Definition
What are Compound Sentences?
A compound sentence is a sentence that consists of two or more independent clauses joined together. These independent clauses are connected using coordinating conjunctions, conjunctive adverbs, or punctuation marks such as commas and semicolons. The purpose of a compound sentence is to express a relationship between the ideas presented in each independent clause.
Method
Constructing Compound Sentences
There are several methods to construct compound sentences, each with its own set of rules and guidelines. The most common methods include using coordinating conjunctions, conjunctive adverbs, and appropriate punctuation to connect independent clauses and form cohesive compound sentences.
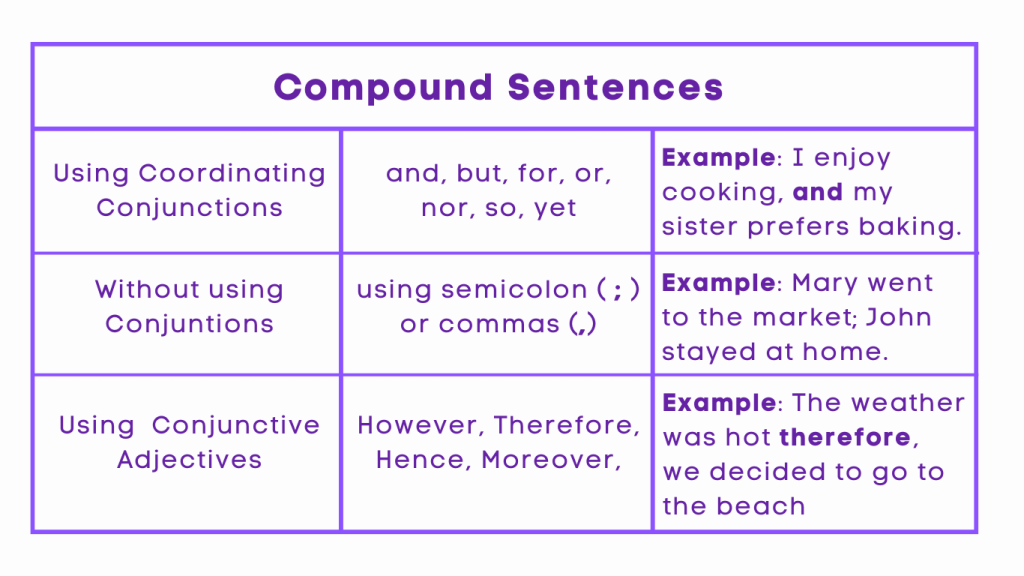
Compound Sentences with a Coordinating Conjunction
One method of constructing a compound sentence is by using coordinating conjunctions such as “and,” “but,” “or,” “for,” “nor,” “so,” and “yet” to connect two independent clauses. For example: “I wanted to go to the movies, but I had to finish my homework.”
Compound Sentences without a Conjunction
Another method involves connecting independent clauses without a coordinating conjunction, using a semicolon or a comma followed by a coordinating conjunction. For example: “She loves to read; he prefers to watch movies.” or “The sun was shining, so we decided to go for a walk.”
Compound Sentences with a Conjunctive Adverb
Additionally, compound sentences can be formed using conjunctive adverbs such as “however,” “therefore,” “moreover,” “nevertheless,” and “consequently” to connect independent clauses. For example: “She studied hard; therefore, she aced the exam.”
Examples
Example 1: I went to the store, and I bought some groceries.
This is a compound sentence because it contains two independent clauses: “I went to the store” and “I bought some groceries.” These clauses are joined by the coordinating conjunction “and,” indicating a relationship of addition or continuation between the actions described in each clause.
Example 2: She loves to read books, but she also enjoys watching movies.
This is also a compound sentence because it consists of two independent clauses: “She loves to read books” and “she also enjoys watching movies.” These clauses are joined by the coordinating conjunction “but,” which signals a contrast or opposition between the activities mentioned in each clause.
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Using Coordinating Conjunctions
Tip: When using coordinating conjunctions to connect independent clauses, remember to place a comma before the conjunction to separate the clauses.
Example: “I wanted to go to the movies, but I had to finish my homework.”
2. Punctuating Compound Sentences
Tip: When connecting independent clauses without a conjunction, use a semicolon or a comma followed by a coordinating conjunction to maintain clarity and coherence.
Example: “She loves to read; he prefers to watch movies.”
3. Employing Conjunctive Adverbs
Tip: When using conjunctive adverbs to connect independent clauses, place a semicolon before the adverb and a comma after it to indicate the relationship between the clauses.
Example: “She studied hard; therefore, she aced the exam.”
4. Differentiating Compound and Complex Sentences
Tip: Compound sentences consist of two or more independent clauses, while complex sentences contain an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
Example: Compound Sentence – “The sun was shining, so we decided to go for a walk.” Complex Sentence – “Although it was raining, we went for a walk.”
5. Maintaining Parallel Structure
Tip: Ensure that the independent clauses in a compound sentence have parallel structure to maintain balance and clarity in the sentence.
Example: “She loves to dance; he prefers to sing.”
Real life application
Story: “The Power of Compound Sentences”
Compound sentences are not just confined to the realm of grammar; they have practical applications in everyday communication and writing. Let’s explore how compound sentences are used in real-life scenarios.
Scenario 1: The Business Presentation
During a business presentation, the speaker used compound sentences to express multiple ideas and emphasize key points. By connecting independent clauses with coordinating conjunctions, the speaker effectively conveyed complex information and maintained the audience’s attention.
Scenario 2: The Persuasive Essay
In a persuasive essay, the writer utilized compound sentences to present compelling arguments and support their claims. By connecting related ideas with conjunctive adverbs, the writer established logical connections and strengthened the overall impact of the essay.
Scenario 3: The Family Dinner Conversation
During a family dinner conversation, family members used compound sentences to share stories, express opinions, and discuss future plans. By employing appropriate punctuation and conjunctions, they engaged in meaningful dialogue and conveyed their thoughts effectively.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends

