Future Tense – Types, Structures and Examples
Table of Contents
Introduction
Future Tense
In the English language, the future tense is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future. It allows us to talk about plans, predictions, and expectations. Understanding the different types of future tense and their structures is essential for effective communication.
Analogy of Definition
What is Future Tense?
The future tense is a verb form that indicates an action or state that will occur after the present time. It is used to express future actions, intentions, or predictions. There are several types of future tense, including simple future, future continuous, future perfect, and future perfect continuous.
Method
Types of Future Tense
1. Simple Future: Used to express actions that will occur in the future.
2. Future Continuous: Used to describe ongoing actions that will happen in the future.
3. Future Perfect: Used to indicate actions that will be completed at a specific time in the future.
4. Future Perfect Continuous: Used to show the duration of an action that will occur before a certain time in the future.
Structure of Future Tense
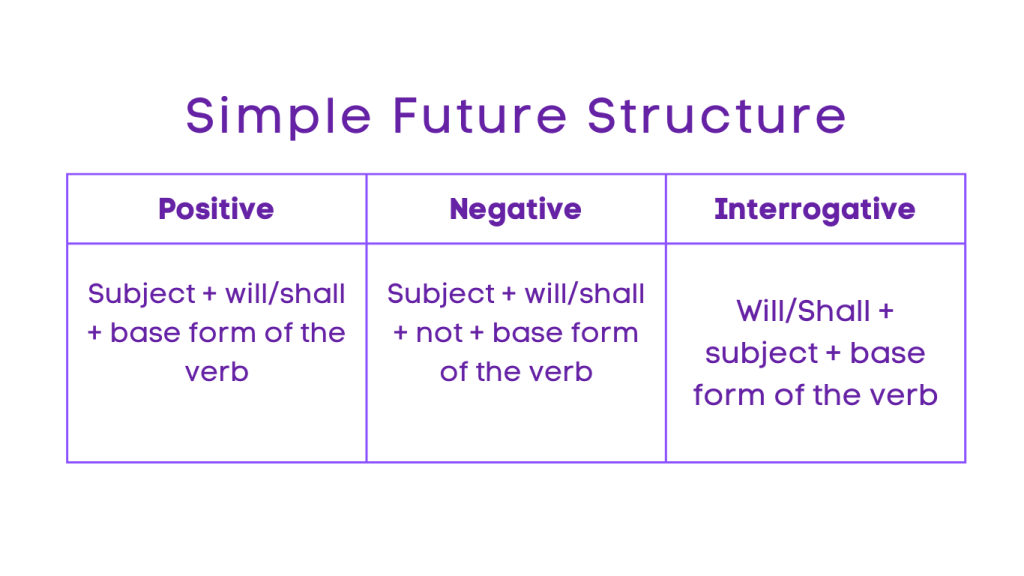
1. Simple Future:
Positive: Subject + will/shall + base form of the verb
Negative: Subject + will/shall + not + base form of the verb
Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + base form of the verb
Negative Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + not + base form of the verb
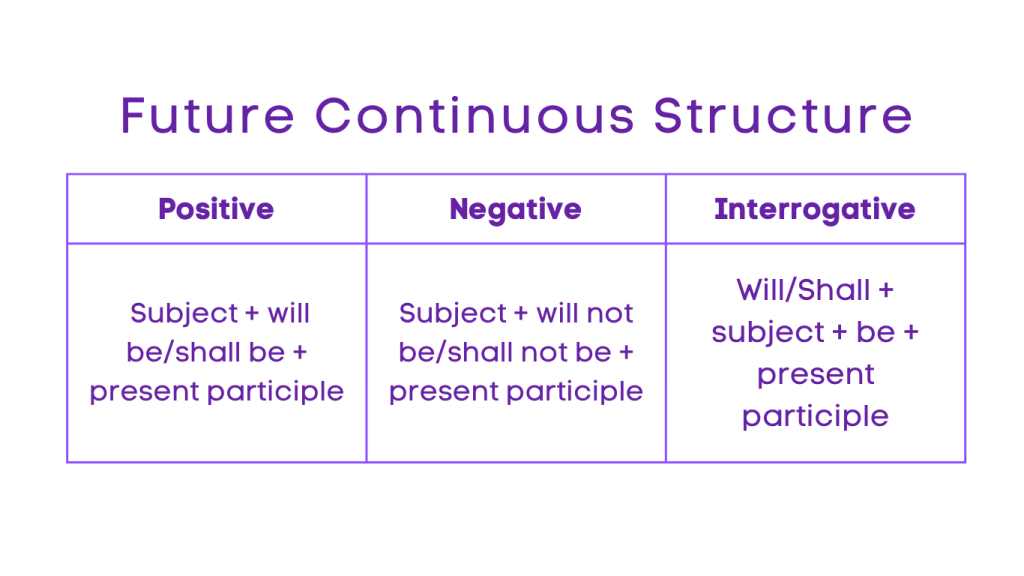
2. Future Continuous:
Positive: Subject + will be/shall be + present participle
Negative: Subject + will not be/shall not be + present participle
Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + be + present participle
Negative Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + not + be + present participle
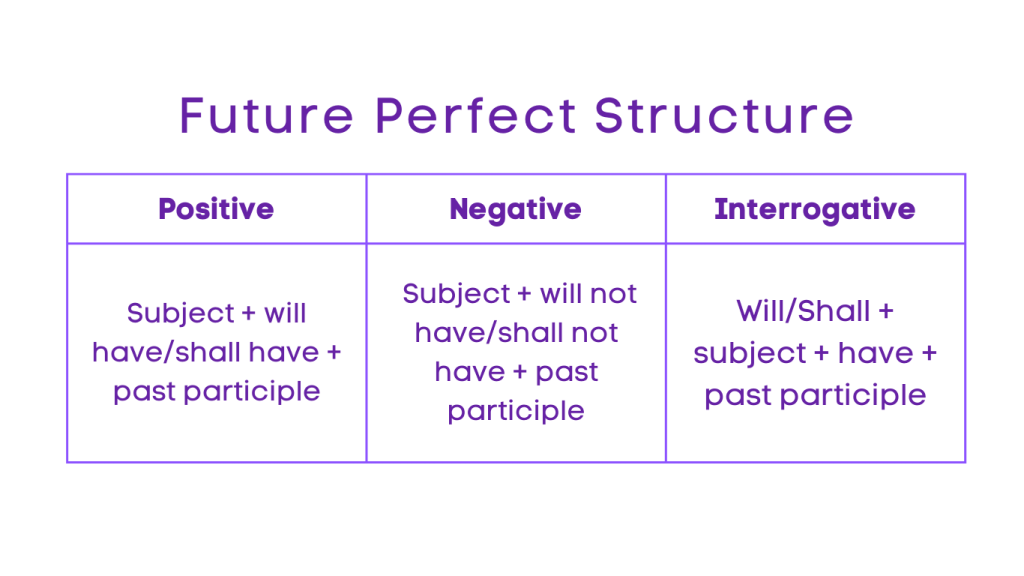
3. Future Perfect:
Positive: Subject + will have/shall have + past participle
Negative: Subject + will not have/shall not have + past participle
Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + have + past participle
Negative Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + not + have + past participle
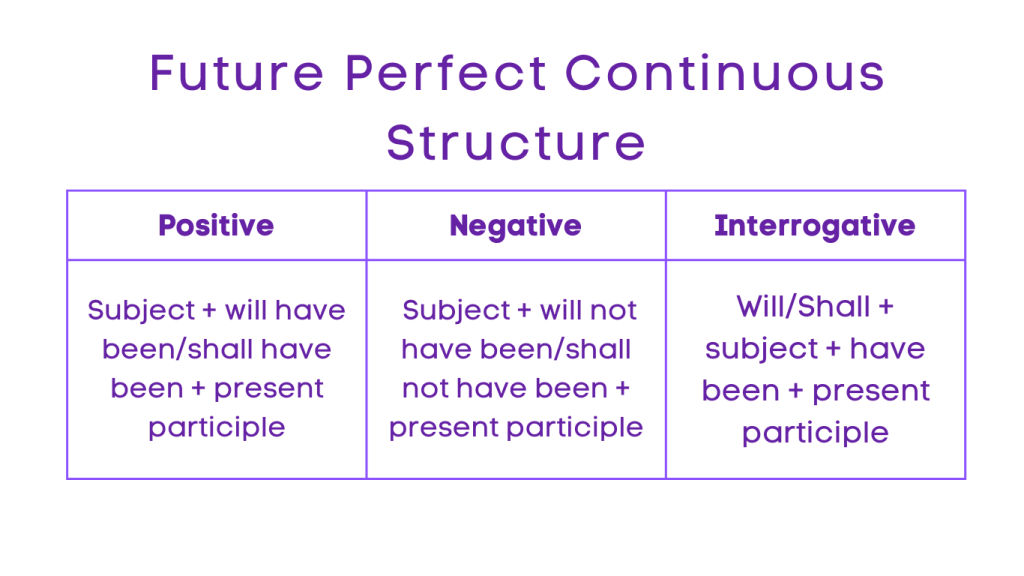
4. Future Perfect Continuous:
Positive: Subject + will have been/shall have been + present participle
Negative: Subject + will not have been/shall not have been + present participle
Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + have been + present participle
Negative Interrogative: Will/Shall + subject + not + have been + present participle
Examples
Simple Future
Positive: She will visit her grandmother tomorrow.
Negative: They will not attend the meeting next week.
Interrogative: Will you join us for dinner tonight?
Negative Interrogative: Will they not complete the project on time?
Future Continuous
Positive: I will be studying for my exam at this time tomorrow.
Negative: He will not be working on the assignment next month.
Interrogative: Will she be waiting for us at the airport?
Negative Interrogative: Will they not be participating in the event?
Future Perfect
Positive: By next year, we will have completed our construction project.
Negative: They will not have finished their work by the deadline.
Interrogative: Will you have submitted your report by Friday?
Negative Interrogative: Will she not have prepared the presentation by then?
Future Perfect Continuous
Positive: By the end of the month, I will have been working here for five years.
Negative: She will not have been living in the city for long.
Interrogative: Will they have been waiting for us for an hour?
Negative Interrogative: Will he not have been studying for the exam?
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Using Simple Future Tense
Scenario: Expressing future actions.
Tip: Use “will” or “shall” followed by the base form of the verb to form positive sentences in simple future tense.
Calculation: She will visit her grandmother tomorrow.
2. Applying Future Continuous Tense
Scenario: Describing ongoing future actions.
Tip: Combine “will be” or “shall be” with the present participle to create positive sentences in future continuous tense.
Calculation: I will be studying for my exam at this time tomorrow.
3. Mastering Future Perfect Tense
Scenario: Indicating completed future actions.
Tip: Use “will have” or “shall have” followed by the past participle to form positive sentences in future perfect tense.
Calculation: By next year, we will have completed our construction project.
4. Understanding Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Scenario: Expressing the duration of future actions.
Tip: Combine “will have been” or “shall have been” with the present participle to create positive sentences in future perfect continuous tense.
Calculation: By the end of the month, I will have been working here for five years.
5. Forming Negative and Interrogative Sentences
Scenario: Using future tense in negative and interrogative forms.
Tip: Add “not” after “will” or “shall” to form negative sentences. In interrogative sentences, invert the subject and “will” or “shall.”
Calculation: Will you join us for dinner tonight? Will they not complete the project on time?
Real life application
Story: “The Future Tense Adventures of Sarah and Mark”
Sarah and Mark, two friends with a passion for language learning, embarked on a journey to explore the practical applications of future tense in various real-life scenarios.
Scenario 1: The Travel Plan
Sarah and Mark were planning a trip to Europe and needed to use the future tense to discuss their itinerary. They used the simple future tense to talk about their upcoming activities, such as “We will visit Paris next week.”
Scenario 2: The Career Aspiration
As they discussed their future career goals, Sarah and Mark used the future continuous tense to describe their ongoing plans, saying, “By this time next year, I will be working at a new company.”
Scenario 3: The Party Invitation
When inviting friends to an upcoming event, Sarah and Mark utilized the future tense in positive and interrogative forms, asking, “Will you attend the party tomorrow?”
Scenario 4: The Project Deadline
In a work-related context, Sarah and Mark used the future perfect tense to discuss their completion of tasks, stating, “They will have completed the project by the end of the month.”
Scenario 5: The Anniversary Celebration
Reflecting on personal milestones, Sarah and Mark employed the future perfect continuous tense to express the duration of future actions, saying, “By next year, they will have been married for twenty years.”
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends

