Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Table of Contents
Introduction
Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers
When dealing with fractions, the concept of improper fractions and mixed numbers often arises. Let’s delve into the realm of converting improper fractions to mixed numbers and explore its significance in mathematical operations. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator (the top number) is greater than or equal to the denominator (the bottom number). For example, \frac{4}{7} is an improper fraction as 7 is greater than 4. A mixed fraction, or mixed number, is a number that combines a whole number and a proper fraction (a fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator). Mixed fractions are used to express quantities that include both whole parts and fractional parts. For instacne 2\frac{4}{7} is a mixed number with whole number,2, and fractional part, \frac{4}{7}.
Analogy of Definition
Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Converting improper fractions to mixed numbers involves expressing the fraction as a whole number combined with a proper fraction. This process allows for a clearer representation of the given fraction.
Method
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
The process of converting an improper fraction to a mixed number entails dividing the numerator by the denominator to obtain the whole number part, and then using the remainder as the numerator of the proper fraction part.
Let’s convert \frac{11}{4} to a mixed number.
Step 1: Divide the numerator by the denominator.
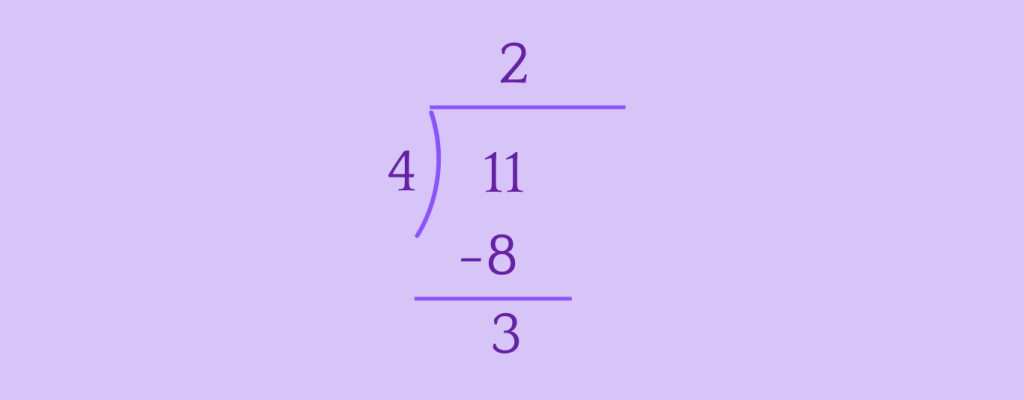
Step 2: Write the mixed number.
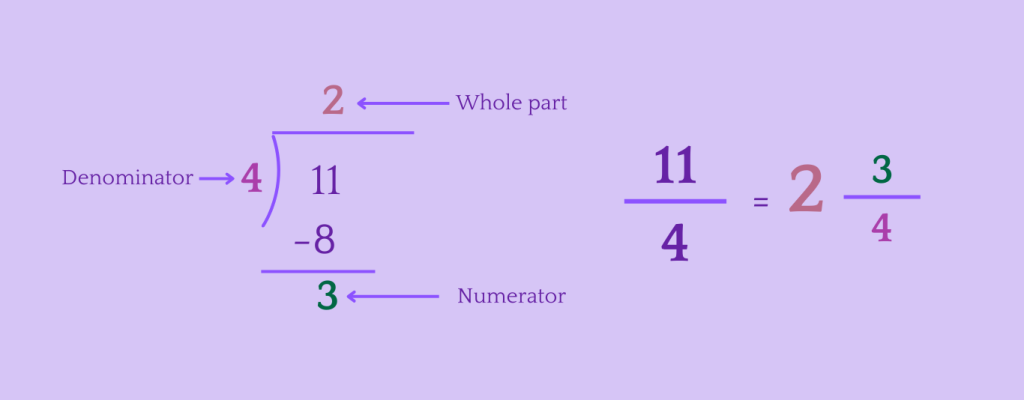
Examples
Converting \frac{7}{3} to a Mixed Number
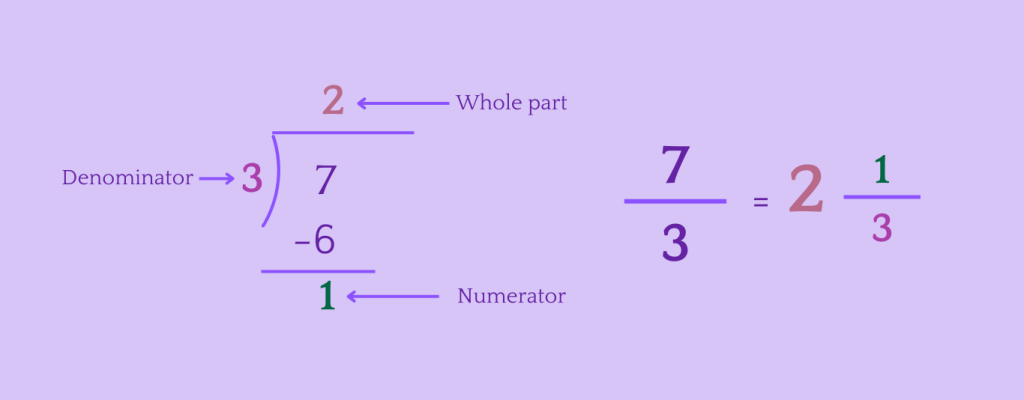
This example demonstrates the process of converting the improper fraction 7/3 to a mixed number. By dividing the numerator by the denominator and expressing the result as a mixed number, the fraction is represented in a clearer and more understandable form, facilitating mathematical operations and real-life applications.
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Visual Representation
Tip: Visualize the division process to convert the improper fraction to a mixed number.
2. Real-Life Application
Tip: Convert the improper fraction to a mixed number to accurately represent the quantity in the recipe.
3. Simplify and Express
Tip: Simplify the fraction and express it as a mixed number for clarity.
Real life application
Scenario: Baking a Cake
When following a recipe to bake a cake, the need to convert improper fractions to mixed numbers arises to accurately measure and combine ingredients. For instance, converting \frac{7}{2} cups of flour to a mixed number results in 3 \frac{1}{2} cups, providing a clear representation of the required quantity.
Scenario: Measuring Length
In carpentry and construction, measurements often involve converting improper fractions to mixed numbers to express lengths and dimensions accurately. Converting \frac{11}{4} feet to a mixed number yields 2 \frac{3}{4} feet, facilitating precise measurements and cuts.
Scenario: Time Calculations
When calculating time intervals, converting improper fractions to mixed numbers aids in expressing durations clearly. For example, converting \frac{9}{2} hours to a mixed number results in 4 \frac{1}{2} hours, simplifying time calculations and scheduling.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends
