Understanding Possessive Nouns: The Basics and Beyond
Table of Contents
Introduction
Possessive Noun
In the English language, possessive nouns play a crucial role in indicating ownership or possession. They are used to show that something belongs to someone or something else. Understanding possessive nouns, their forms, and their usage is essential for effective communication and writing.
Analogy of Definition
What is A Possessive Noun?
A possessive noun is a noun that shows ownership or possession. It is often formed by adding an apostrophe and the letter “s” (‘s) to the end of the noun. For plural nouns, the apostrophe is placed after the “s” at the end of the word. Possessive nouns can also function as possessive adjectives or possessive pronouns, indicating the relationship between the noun and the owner.
Method
Forming Possessive Nouns
The possessive form of a singular noun is created by adding an apostrophe and “s” (‘s) to the end of the word. For plural nouns that end in “s,” the possessive form is indicated by adding an apostrophe after the “s.” For irregular possessive nouns, the form varies and must be memorized.
Possessive Adjective
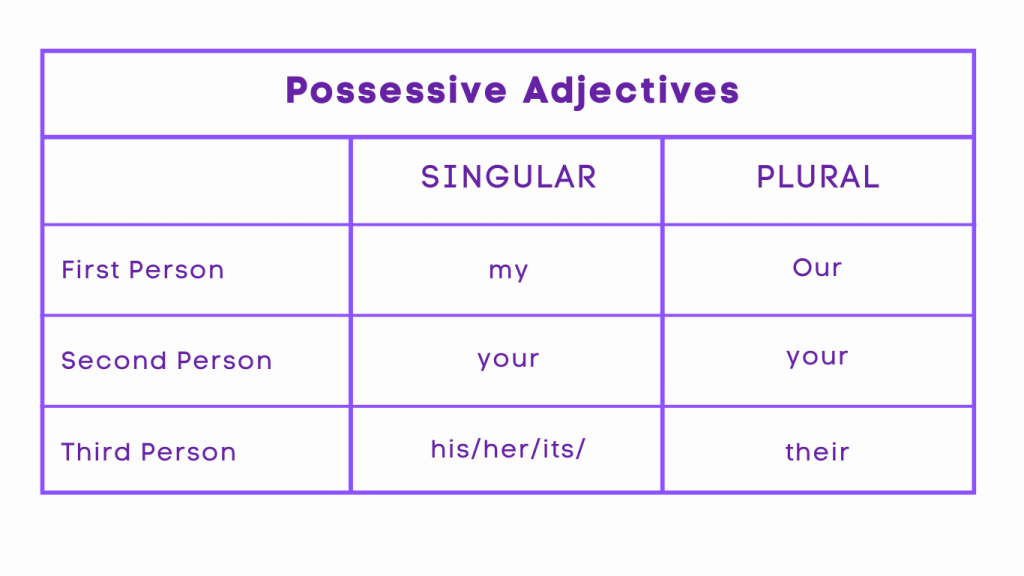
Similar to possessive nouns, possessive adjectives express ownership or close association. They align with English pronouns in terms of person, gender, and number. Unlike possessive nouns, possessive adjectives are not marked with apostrophes. This distinction is particularly important with the possessive adjective ‘its,’ often mistaken for the contraction ‘it’s,’ meaning ‘it is.
Example:
Their house is big.
In this sentence, “their” is a possessive adjective indicating that the house belongs to a group of people.
Possessive Pronoun
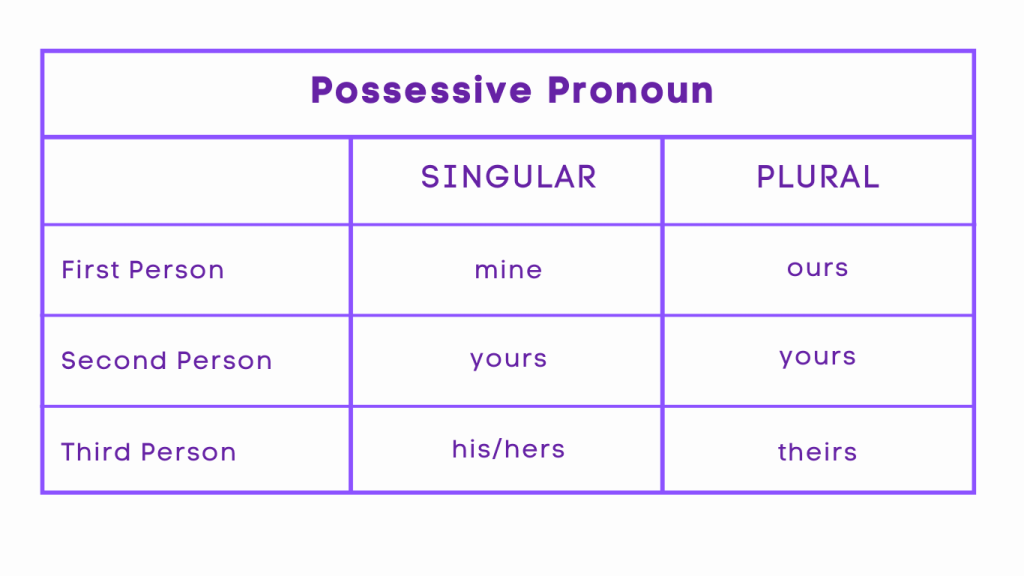
Possessive pronouns serve as the noun form of pronouns, indicating possession. Similar to regular pronouns, they substitute for other nouns to prevent redundancy. Contrary to other possessive nouns, possessive pronouns are not positioned before the object of possession. Typically, the referent is introduced earlier, and the possessive pronoun replaces it to avoid repetition. It’s important to differentiate between possessive pronouns and possessive adjectives. Possessive pronouns function as nouns, not adjectives, and should be used accordingly.
Example:
“The book is hers.”
In this sentence, “hers” is a possessive pronoun indicating that the book belongs to her.
Irregular Possessive Nouns
While most possessive nouns follow the standard rules for forming the possessive form, there are some irregular possessive nouns that do not follow these rules. The formation of possessive irregular plural nouns varies depending on whether they already end in an “s.”For example, “children’s” is the possessive form of “children,” and “women’s” is the possessive form of “women.” It is important to be familiar with these irregular forms to use possessive nouns correctly.
Examples
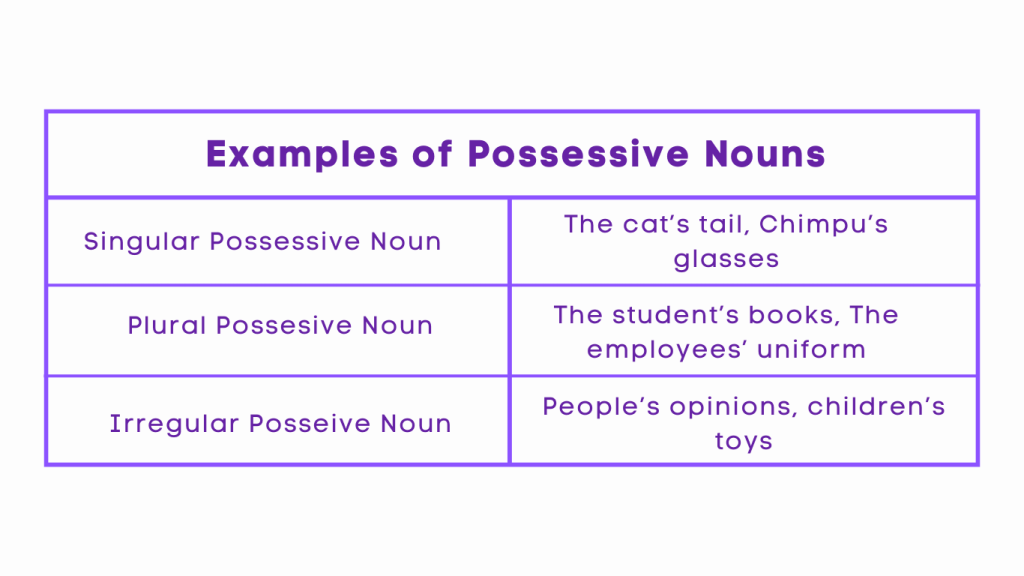
Examples of Possessive Nouns
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Singular Possessive Nouns
Tip: To form a singular possessive noun, add an apostrophe and “s” (‘s) to the end of the word.
Example: The cat’s tail
2. Plural Possessive Nouns
Tip: For plural nouns that end in “s,” add an apostrophe after the “s” to indicate possession.
Example: The students’ books
3. Irregular Possessive Nouns
Tip: Irregular possessive nouns have unique forms that must be memorized.
Example: The children’s toys
4. Possessive Adjectives
Tip: Possessive adjectives, such as “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their,” are used to indicate ownership or possession.
Example: Her book
5. Possessive Pronouns
Tip: Possessive pronouns, such as “mine,” “yours,” “his,” “hers,” “its,” “ours,” and “theirs,” replace the noun and show ownership.
Example: The book is mine.
Real life application
Story: “The Possessive Adventures of Emily and Max”
Emily and Max, two curious students, embarked on a journey to explore the world of possessive nouns and their applications in everyday life.
Adventure 1: The Family’s Farm
Emily and Max visited a farm where they encountered various signs indicating ownership. They saw signs that read “The cow’s milk” and “The farmer’s tools,” showcasing the use of possessive nouns to denote possession.
Adventure 2: The Students’ Art Exhibit
At an art exhibit, Emily and Max observed labels on artwork that displayed the artists’ names with apostrophes to indicate ownership. They learned how possessive nouns are used to attribute creations to their creators.
Adventure 3: The Teacher’s Classroom
In their classroom, Emily and Max noticed the teacher’s desk and the students’ lockers, recognizing how possessive nouns are used to show ownership of specific items within a shared space.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends






