Understanding the Concept of Present Tense
Table of Contents
Introduction
Present Tense
In the English language, the concept of tense refers to the time of an action or event. Present tense specifically deals with actions or events that are happening now or are generally true. It is a fundamental aspect of English grammar and is used to convey information about the present moment.
Analogy of Definition
What is Present Tense?
The present tense is used to describe actions, events, or situations that are currently happening, habitual actions, general truths, or future actions that are scheduled. It is divided into four main types: simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous.
Method
Types of Present Tense
The four types of present tense are as follows:
1. Simple Present Tense: Used to express habitual actions, general truths, or facts that are true at the present moment. Example: “She reads books every day.”
2. Present Continuous Tense: Describes actions that are happening at the moment of speaking or ongoing actions in the present. Example: “He is studying for his exam right now.”
3. Present Perfect Tense: Indicates actions that were completed at an unspecified time in the past, often with a connection to the present. Example: “I have finished my homework.”
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense: Shows actions that started in the past and continue up to the present moment or have recently stopped. Example: “They have been playing football for two hours.”
Structure of Present Tense for Each Type
Each type of present tense has a specific structure for forming positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative sentences.
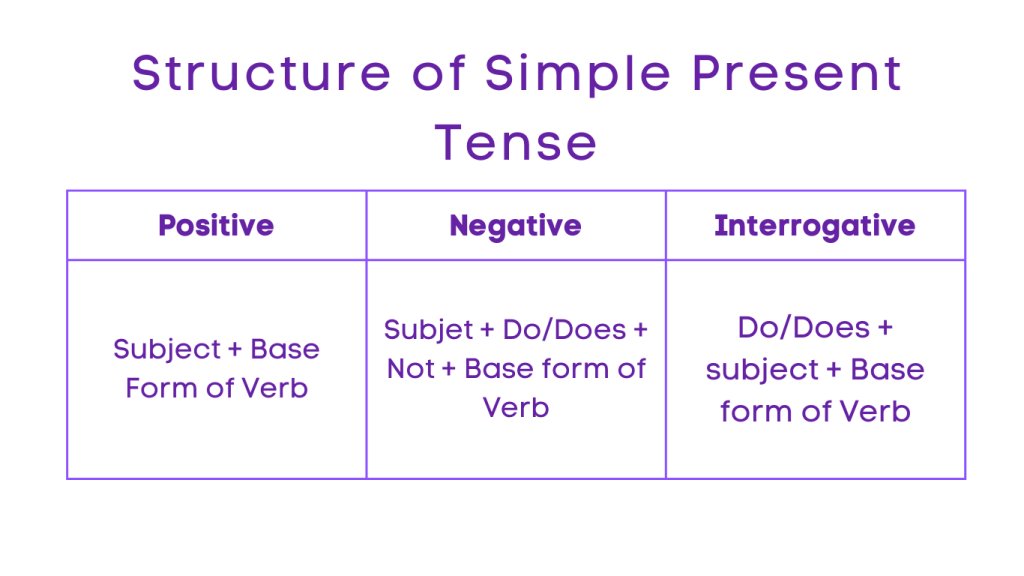
1. Simple Present Tense
Positive: Subject + Base Form of Verb
Negative: Subject + Do/Does + Not + Base Form of Verb
Interrogative: Do/Does + Subject + Base Form of Verb?
Negative Interrogative: Do/Does + Subject + Not + Base Form of Verb?
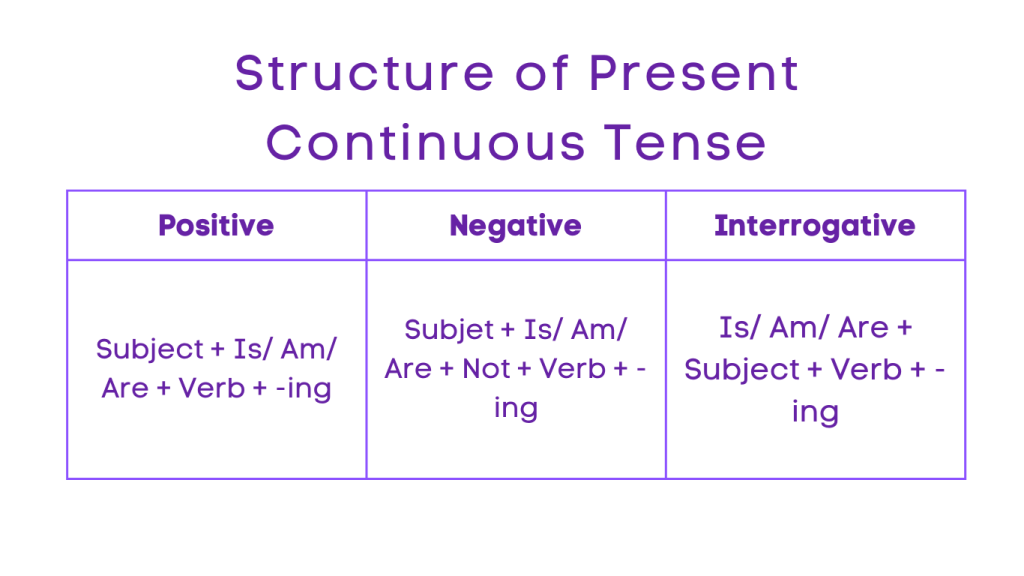
2. Present Continuous Tense
Positive: Subject + Am/Is/Are + Verb + -ing
Negative: Subject + Am/Is/Are + Not + Verb + -ing
Interrogative: Am/Is/Are + Subject + Verb + -ing?
Negative Interrogative: Am/Is/Are + Subject + Not + Verb + -ing?
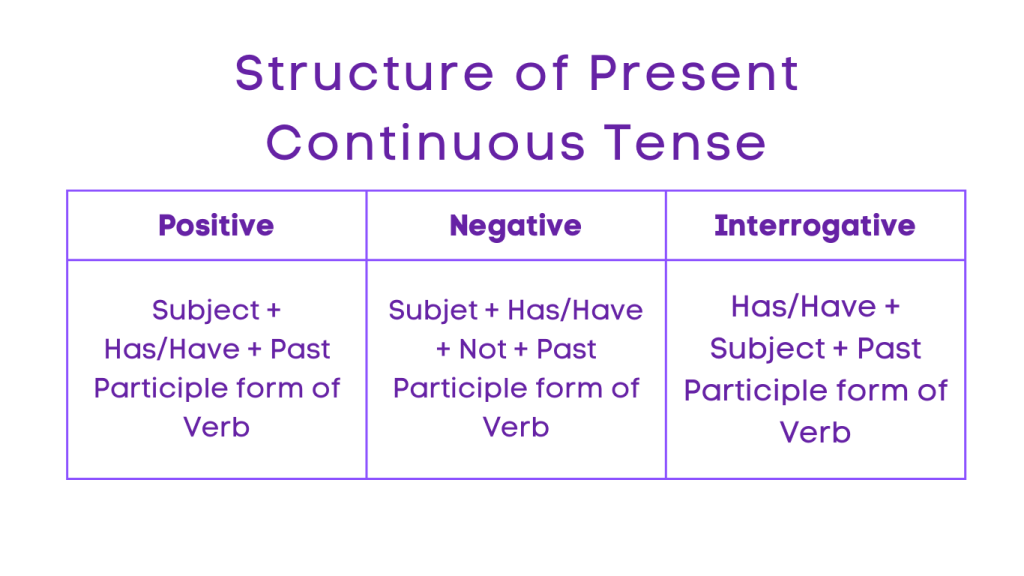
3. Present Perfect Tense
Positive: Subject + Has/Have + Past Participle
Negative: Subject + Has/Have + Not + Past Participle
Interrogative: Has/Have + Subject + Past Participle?
Negative Interrogative: Has/Have + Subject + Not + Past Participle?
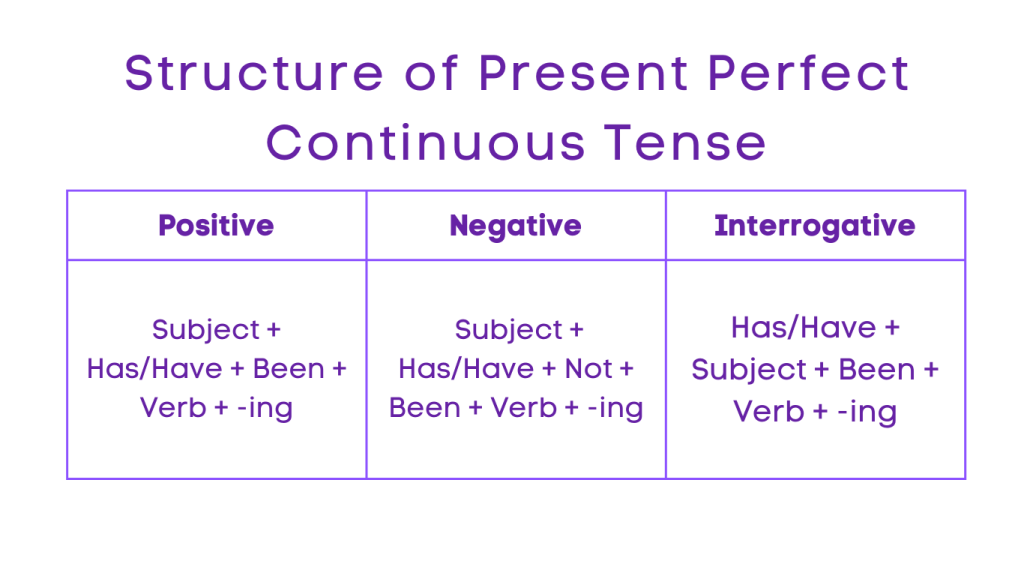
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Positive: Subject + Has/Have + Been + Verb + -ing
Negative: Subject + Has/Have + Not + Been + Verb + -ing
Interrogative: Has/Have + Subject + Been + Verb + -ing?
Negative Interrogative: Has/Have + Subject + Not + Been + Verb + -ing?
Examples
Examples of Present Tense:
1. Simple Present Tense
Positive: She sings.
Negative: She does not sing.
Interrogative: Does she sing?
Negative Interrogative: Does she not sing?
2. Present Continuous Tense
Positive: They are playing.
Negative: They are not playing.
Interrogative: Are they playing?
Negative Interrogative: Are they not playing?
3. Present Perfect Tense
Positive: He has finished.
Negative: He has not finished.
Interrogative: Has he finished?
Negative Interrogative: Has he not finished?
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Positive: We have been waiting.
Negative: We have not been waiting.
Interrogative: Have we been waiting for long?
Negative Interrogative: Have we not been waiting for long?
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Simple Present Tense
Tip: Use the base form of the verb with the subject to create positive sentences in simple present tense.
2. Present Continuous Tense
Tip: Add “not” after the helping verb to create negative sentences in present continuous tense.
3. Present Perfect Tense
Tip: Invert the position of the helping verb and the subject to form interrogative sentences in present perfect tense.
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Tip: Combine the rules for forming negative and interrogative sentences to create negative interrogative sentences in present perfect continuous tense.
5. Negative Interrogative Sentences
Tip: Combine the rules for forming negative and interrogative sentences to create negative interrogative sentences in present tense.
Real life application
Story: “The Present Tense Chronicles”
The present tense plays a crucial role in various real-life scenarios, as demonstrated in the following examples:
Scenario 1: Daily Routines
In everyday conversations, people use the simple present tense to describe their daily routines and habits. For example, “I wake up at 7 AM every day.”
Scenario 2: Current Actions
When reporting on ongoing events or actions happening at the moment, the present continuous tense is used. For instance, “They are playing football in the park.”
Scenario 3: Recent Events
The present perfect tense is employed to talk about recent events or actions that have an impact on the present. An example would be, “She has finished her homework.”
Scenario 4: Duration of Actions
The present perfect continuous tense is used to indicate the duration of actions that started in the past and continue into the present. For instance, “We have been waiting for the bus for an hour.”
Scenario 5: Negative Statements
In situations where negation is required, the simple present tense is used to express negative statements. For example, “He does not like spicy food.”
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends






