Prime Factorization
Table of Contents
Introduction
Prime Factorization
In the realm of mathematics, the concept of prime factorization plays a crucial role in breaking down numbers into their fundamental building blocks. By identifying the prime factors of a number, we gain valuable insights into its unique composition and properties. Let’s delve into the world of prime factorization and explore its significance in solving mathematical puzzles.
Analogy of Definition
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization involves expressing a composite number as the product of its prime factors. A prime factor is a number that is divisible only by 1 and itself, such as 2, 3, 5, 7, and so on. By decomposing a number into its prime factors, we can understand its prime factorization.
Method
Methods of Prime Factorization
There are several methods to find the prime factorization of a number. One common method is the factor tree, which involves breaking down a number into its prime factors through a branching structure. Another method is the division method, where we repeatedly divide the number by prime numbers until we obtain the prime factorization.
Factor Tree Method
In prime factorization using the factor tree method, we break down a number into its prime factors by repeatedly finding pairs of factors and factoring them until we only have prime numbers left. This method involves breaking down a given number into its prime factors by repeatedly finding pairs of factors and factoring them until only prime numbers remain.. Let’s illustrate this process with an example:
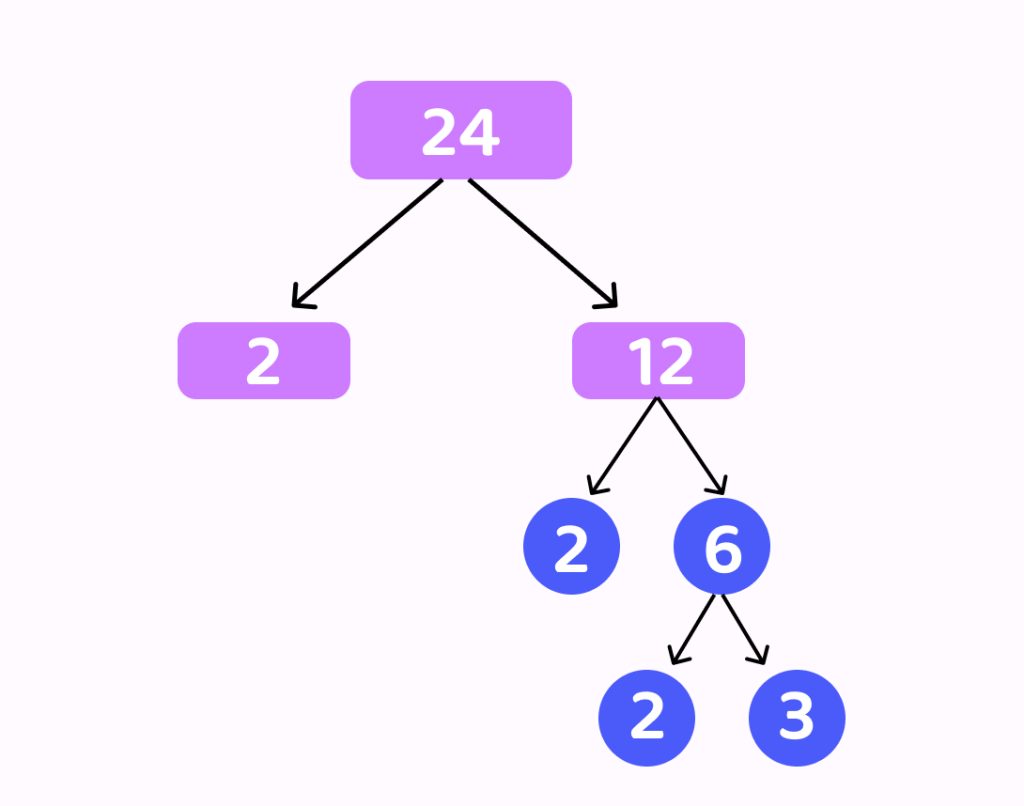
Example: Find the prime factorization of 24 using the factor tree method.
Step 1: Begin by placing the number 24 at the top of the factor tree.
Step 2: Identify a pair of factors for 24. One possible pair is 6 and 4, as 6 multiplied by 4 equals 24.
Step 3: Factorize 6 and 4 into their prime factors. For 6, we have 2 × 3, and for 4, we have 2 × 2.
Step 4: Continue breaking down any composite factors until only prime numbers remain. Both 2 and 3 are prime, so no further factorization is needed.
Step 5: Write down the prime factors obtained from the factorization. For 24, the prime factors are 2, 2, 2, and 3.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 24 using the factor tree method is 2 × 2 × 2 × 3.
This example demonstrates the process of prime factorization using the factor tree method for the number 24.
Division Method
The division method for finding prime factors involves repeatedly dividing a number by prime numbers until only prime factors remain. This systematic approach is efficient and particularly useful for large numbers, providing a clear path to determining the prime factors of a given number.
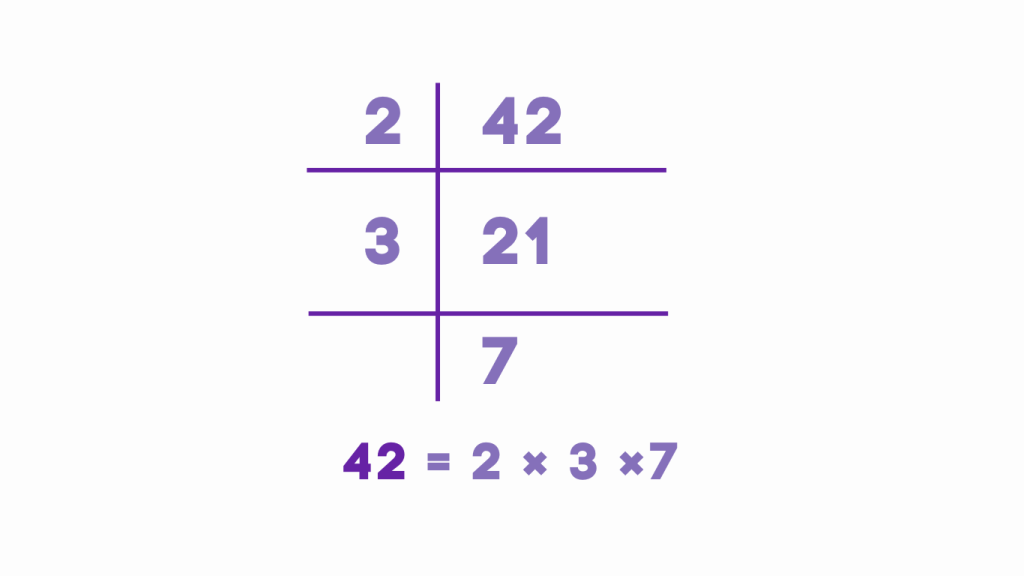
Example: Let’s prime factorize the number 42 using the division method.
Step 1: Begin by dividing 42 by the smallest prime number, which is 2. 42 divided by 2 equals 21.
Step 2: Since 21 is not divisible by 2, move to the next smallest prime number, which is 3. Divide 21 by 3, which equals 7.
Step 3: Since 7 is a prime number, and it cannot be divided further, we stop.
Step 4: Multiply all the prime factors obtained from the divisions. The prime factorization of 42 is 2 × 3 × 7.
Examples
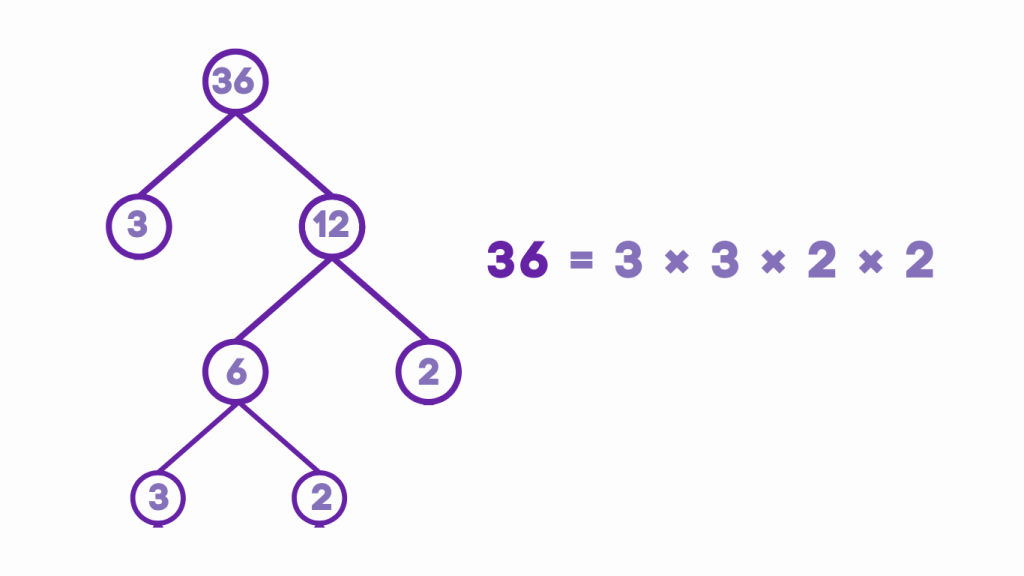
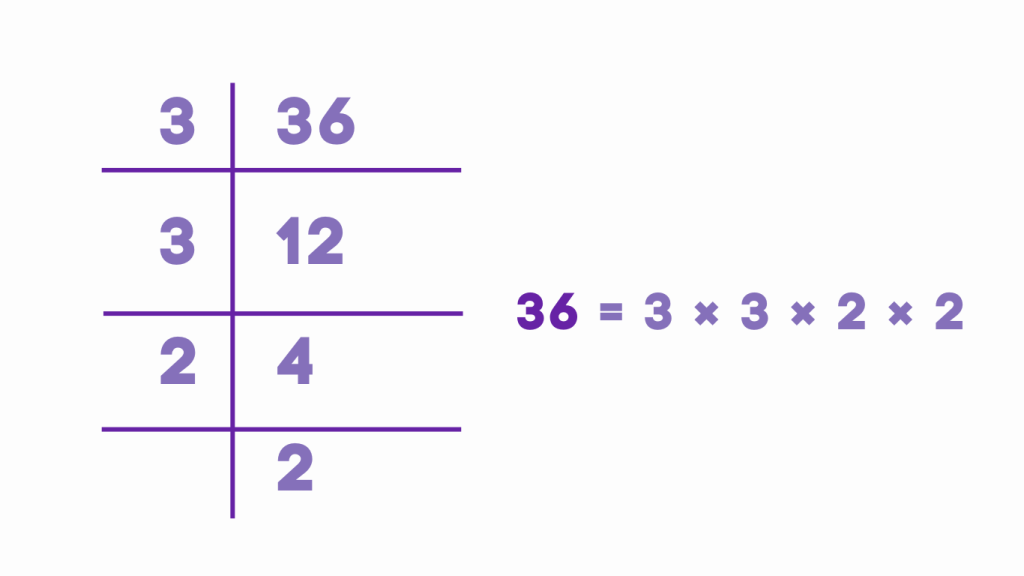
Example: Finding the Prime Factorization of 36
Using Factor Tree Method
Using Division Method
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Start with Small Primes
Tip: When prime factorizing a number, begin by dividing it by the smallest prime numbers (2, 3, 5, 7, etc.). This often simplifies the process and helps identify prime factors quickly.
2. Use Factor Trees
Tip: Draw a factor tree to visually break down a number into its prime factors. This method can be particularly helpful for large numbers or complex factorizations.
3. Trial and Error
Tip: If you’re unsure which prime number to divide by next, try dividing the number by the smallest prime factors and see if any of them divide evenly. If not, move to the next prime number.
4. Know Prime Numbers
Tip: Familiarize yourself with the first few prime numbers (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.) to recognize them quickly during factorization.
5. Factorization Tables
Tip: Refer to factorization tables or charts to find common prime factors of numbers. This can save time, especially when dealing with frequently occurring numbers.
Real life application
The Prime Factorization Quest
Embark on a journey with Sarah and David as they encounter real-life scenarios where prime factorization becomes the key to unlocking mysteries and solving challenges.
Challenge 1: The Fraction Dilemma
Sarah was tasked with simplifying fractions in her math class. By using prime factorization, she was able to find the greatest common divisor of the numerator and denominator, allowing her to simplify the fractions effectively.
Challenge 2: The Puzzle of Divisibility
David encountered a series of numbers and needed to determine if they were divisible by a specific factor. By applying prime factorization, he could quickly identify the prime factors of the numbers and determine their divisibility.
Challenge 3: The Cryptography Conundrum
In a cryptography challenge, Sarah and David needed to factorize large numbers to crack codes and decipher hidden messages. Prime factorization enabled them to unravel the secrets hidden within the numbers.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends
