Understanding Pronouns – Meaning, Types and Examples
Table of Contents
Introduction
Pronouns
Pronouns are an integral part of language and communication. They serve as substitutes for nouns, making sentences more efficient and less repetitive. Let’s delve into the world of pronouns and explore their various types and functions.
Analogy of Definition
What are Pronouns?
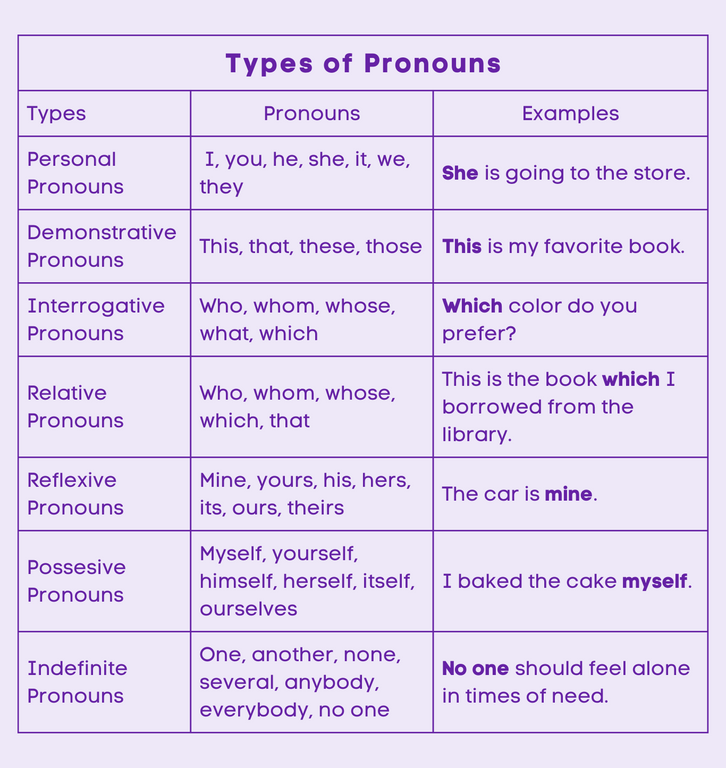
Pronouns are words that take the place of nouns in a sentence. They can represent people, places, things, or ideas, and are categorized into different types based on their functions and usage. There are several types of pronouns, including personal pronouns, reflexive pronouns, relative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. Each type serves a unique purpose in language and communication.
Method
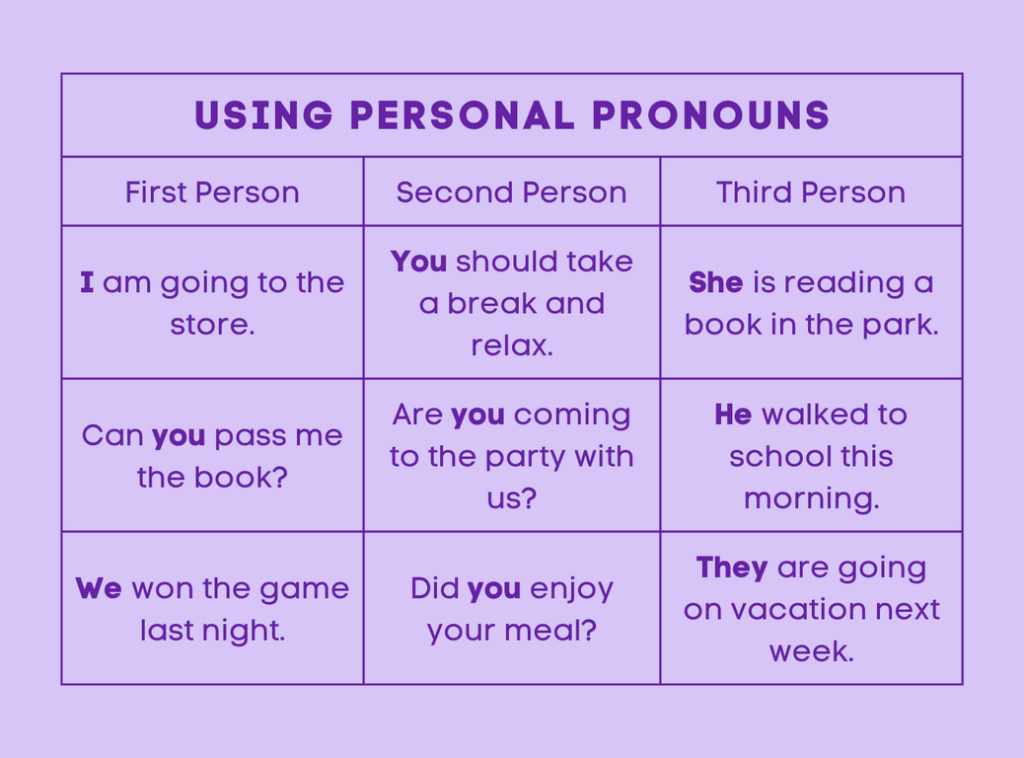
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are fundamental in language, particularly as they adapt based on the grammatical person involved—whether it’s the speaker (first person), the listener (second person), or someone or something being discussed (third person). These pronouns reflect the dynamic nature of communication, changing form to accurately represent different perspectives. Here are examples of some common personal pronouns:
- She/Her
- He/His
- I/Me
- It
- We/Us
- They/Them
- You
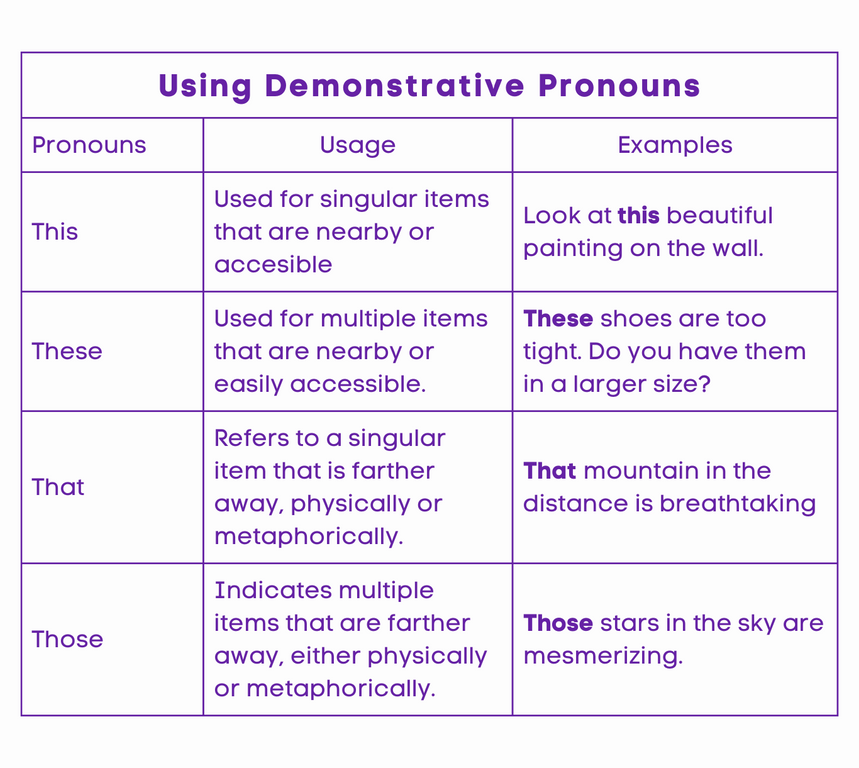
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns, such as “that,” “this,” “these,” and “those,” serve to directly indicate or replace an antecedent—an earlier noun or noun phrase in the sentence that the pronoun refers to.
These pronouns vary based on the number and proximity of the items they refer to. Here’s a simple guide to help you understand the proper way of using demonstrative pronouns.
Interrogative pronouns
Interrogative pronouns, like “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “what,” and “which,” serve the purpose of asking questions or seeking specific information about people or things. These pronouns facilitate inquiries and aid in gathering relevant details.
Here are a few examples of interrogative pronouns
- Who is coming to the party tonight?
- To whom should I address the letter?
- Whose phone is ringing?
- What time does the movie start?
- Which movie did you watch last night?
In this way, we can use the interrogative pronouns to form questions.
Who vs. Whom
The difference between “who” and “whom” can be a bit tricky, but it’s all about understanding their roles in a sentence.
Who: We use “who” when you are talking about the subject of a sentence. Think of it as the person doing the action
Example: Who is coming to the party?
In this sentence, “who” is the subject because it refers to the person performing the action of coming to the party.
Whom: We use “whom” when you are talking about the object of a verb or preposition. Think of it as the person receiving the action.
Example: To whom did you give the gift?
In this sentence, “whom” is the object of the preposition “to” because it receives the action of giving the gift.
In summary, we use “who” when talking about the subject and “whom” when talking about the object. With a bit of practice, it becomes easier to choose the correct one!
Relative pronouns
Relative pronouns serve as connectors between relative clauses and independent clauses, offering additional information about something previously mentioned. These pronouns encompass words such as:
- Who
- Whom
- Which
- That
We usually use “who” to refer to people, while “which” and “that” refer to animals or things. Let’s explore how these relative pronouns function in sentences:
Example: The person who called earlier didn’t leave a message.
In this sentence, “who” introduces additional information about the person who called.
Example: All the cats that were adopted today will be well cared for.
Here, “that” connects the relative clause (“that were adopted today”) to the independent clause (“All the cats”).
Possesive Pronoun
Possessive pronouns, indicate ownership or possession by replacing a noun. They stand alone to show who something belongs to. These pronouns include:
- Mine
- Yours
- Ours
- His
- Hers
- Theirs
- Its
Here are a few examples:
- The book on the table is mine.
- Is this pen yours?
- The house with the red door is theirs
Reflexive pronoun
Reflexive pronouns are a type of personal pronouns that end in “-self” or “-selves”:
- Myself
- Himself
- Herself
- Itself
- Yourself
- Yourselves
- Oneself
- Ourselves
- Themselves
These pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence or clause and are often used as the object of a verb or preposition. Here are a few examples:
- He reminded himself to double-check the documents before the meeting.
- We organized the event all by ourselves, from planning to execution.
- The cat groomed itself meticulously after getting caught in the rain.
Indefinite pronouns
Indefinite pronouns serve as general references to people or things without the need for specific identification or previous mention. When we use such pronouns as the subject, usually singular verb forms are use. Here are some common indefinite pronouns:
- none
- some
- anybody
- everybody
- no one
- other
We can use indefinite pronouns in the following manner:
- One should always strive to do their best.
- None of the students brought their homework.
- Everybody loves a good story.
- Is anybody here willing to volunteer?
Examples
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Using Reflexive Pronouns
Tip: Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object of a sentence are the same.
2. Relative Pronouns in Action
Tip: Relative pronouns connect clauses and provide additional information about a noun.
3. Understanding Indefinite Pronouns
Tip: Indefinite pronouns refer to nonspecific people or things.
4. Using Who
Tip: If you can replace “who” with “he,” “she,” or “they,” use “who.”
5. Using Whom
Tip: If you can replace “whom” with “him,” “her,” or “them,” use “whom.”
Real life application
Real-Life Applications of Pronouns:,
Scenario: Everyday Conversations
In everyday conversations, pronouns are used extensively to avoid repetition and maintain a smooth flow of communication. Whether it’s discussing plans with friends or sharing stories with family, pronouns play a vital role in effective communication.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends
