Understanding Rational Numbers: Definition and Properties
Table of Contents
Introduction
Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are an integral part of the number system, encompassing a wide range of values that can be expressed as a fraction. Let’s delve into the realm of rational numbers and explore their significance in the realm of mathematics.
Analogy of Definition
What are Rational Numbers?
Rational numbers are defined as any number that can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not equal to 0. In simpler terms, rational numbers are those that can be written as a fraction of two integers.
Method
Types of Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction where the numerator and denominator are both integers, and the denominator is not zero. Here are the different types of rational numbers explained in a simple manner with examples:
1. Positive Rational Numbers: These are rational numbers greater than zero.
Example:\frac{3}{4}, \frac{5}{6}
2. Negative Rational Numbers: These are rational numbers less than zero.
Example: –\frac{2}{3}, –\frac{5}{4}
3, Whole Numbers: These are rational numbers that don’t have a fractional part.
Example: 2 = \frac{2}{1}, 9 = \frac{9}{1}
4. Integers: These include both positive and negative whole numbers, as well as zero.
Example: −3, 0, 5
5. Fractions: All fractions fall under the category of rational numbers. Additionally, rational numbers also include decimal numbers that terminate or repeat.
Example: \frac{1}{2}, \frac{7}{5}, 0.23. 0.58, 0.121212
Rational and Irrational Numbers
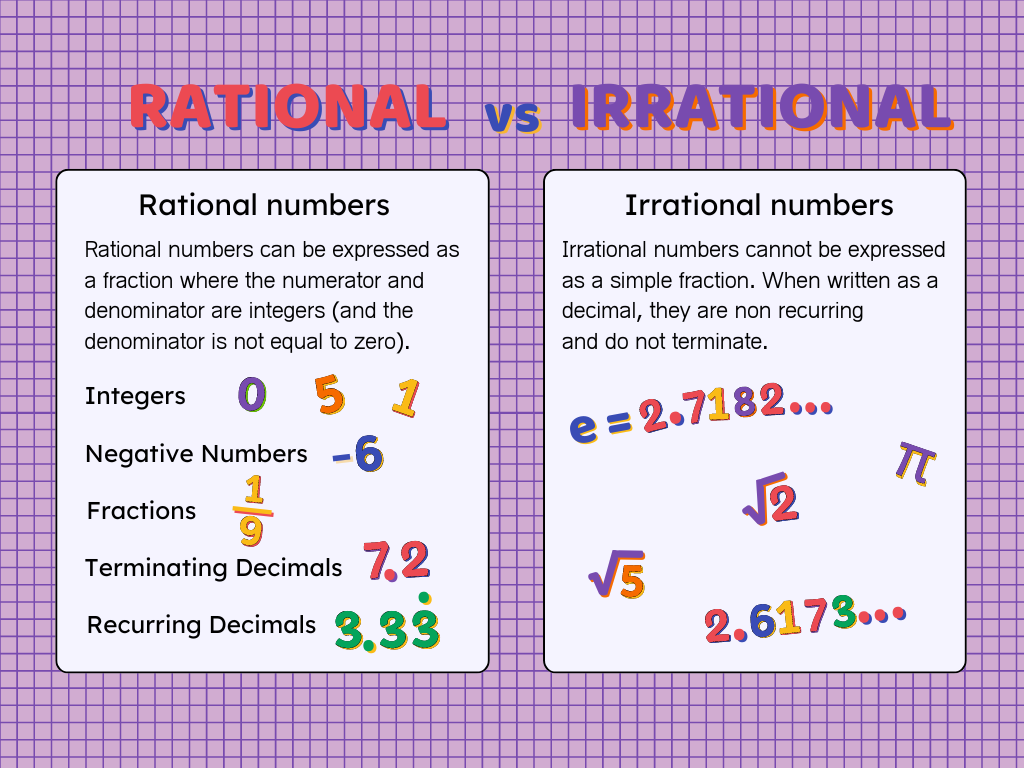
Examples
Example 1: Adding rational numbers
Calculation: \frac{3}{4} + \frac{1}{2} = \frac{5}{4}
Example 2: Multiplying rational numbers
Calculation: \frac{2}{3} × \frac{5}{7} = \frac{10}{21}
Example 3: Dividing rational numbers
Calculation: \frac{4}{5} ÷ \frac{2}{3} = \frac{12}{10}
These examples illustrate the application of rational numbers in various mathematical operations such as addition, multiplication, and division. By demonstrating the manipulation of rational numbers, these examples showcase the practical utility of rational numbers in solving mathematical problems and real-world scenarios.
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Rational and Irrational Numbers
Tip: Remember that rational numbers can be expressed as fractions or terminating/repeating decimals, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal representations.
2. Whole Numbers and Integers
Tip: All whole numbers and integers are rational numbers. For example, 5, -3, 0 are all rational numbers because they can be expressed as fractions (\frac{5}{1}, –\frac{3}{1}, \frac{0}{1}).
3. Fractions
Tip: Any fraction where the numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero, is a rational number. For example, \frac{3}{4}, –\frac{2}{5},\frac{7}{2} are all rational numbers.
4. Repeating and Terminating Decimals
Tip: Decimal numbers that either terminate (end) or repeat are also rational numbers. For example, 0.25 (terminating) and 0.333… (repeating) are rational numbers because they can be expressed as fractions (\frac{1}{4} and \frac{1}{3} respectively).
5. Roots of Perfect Squares
Tip: The square root of any perfect square is a rational number. For example, √9 = 3 and √16 = 4 are rational numbers because they can be expressed as fractions (\frac{3}{1} and \frac{4}{1} respectively).
Real life application
Scenario: Budgeting for a Trip
Planning a trip involves budgeting for expenses such as accommodation, food, and transportation. Rational numbers are utilized to calculate costs, allocate funds, and manage the overall budget effectively.
Scenario: Cooking and Baking
Recipes often require precise measurements of ingredients, which are represented by rational numbers. Whether it’s measuring flour, sugar, or liquids, rational numbers play a crucial role in ensuring accurate and delicious culinary creations.
Scenario: Scientific Calculations
In scientific experiments and calculations, rational numbers are used to represent measurements, quantities, and ratios. From chemical compositions to physical dimensions, rational numbers are indispensable in scientific endeavors.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends
