Understanding the Concept of Past Tense
Introduction
Past Tense
In the English language, the past tense is used to indicate an action, event, or state that has already occurred or happened in the past. Understanding tenses is essential for accurately expressing actions and states of being in relation to different points in time. It allows us to express and communicate about past experiences, actions, or situations.
Analogy of Definition
What is Past Tense?
The past tense is a grammatical form that denotes an action that has already taken place. It is used to describe events that have happened at a specific time in the past or over a period of time in the past.
Method
Types and Structure of Past Tense
There are four main types of past tense: simple past, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous. Each type has its own structure and usage in expressing past actions and events.
Each type of past tense has a specific structure for forming positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative sentences. Understanding the structure of past tense is essential for using it correctly in different contexts.
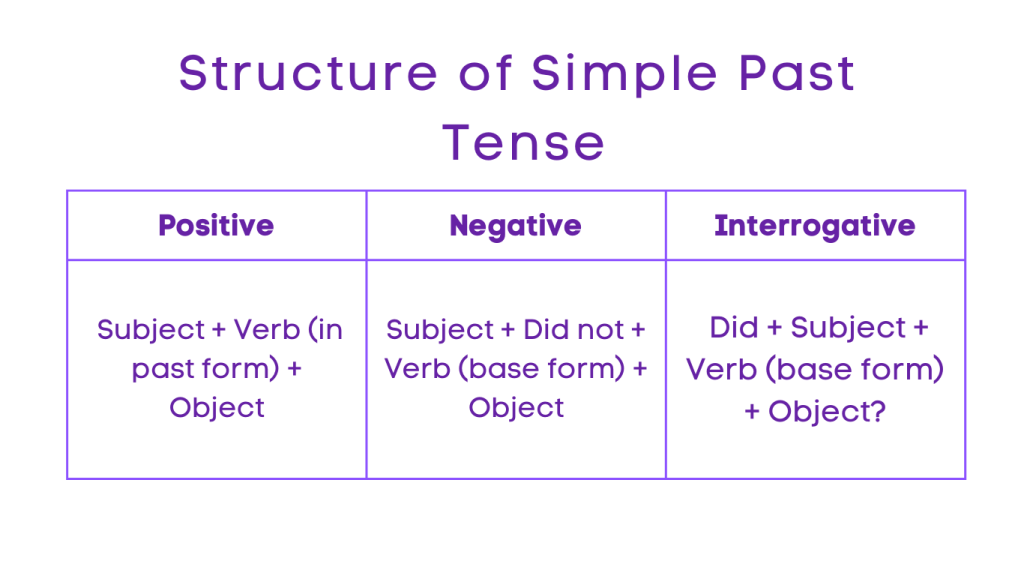
Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense is used to describe actions that were completed at a specific time in the past. It is formed by adding “-ed” to regular verbs, while irregular verbs have specific past forms.
Structure:
Positive: Subject + Verb (in past form) + Object
Negative: Subject + Did not + Verb (base form) + Object
Interrogative: Did + Subject + Verb (base form) + Object?
Negative Interrogative: Did not + Subject + Verb (base form) + Object?
Past Continuous Tense
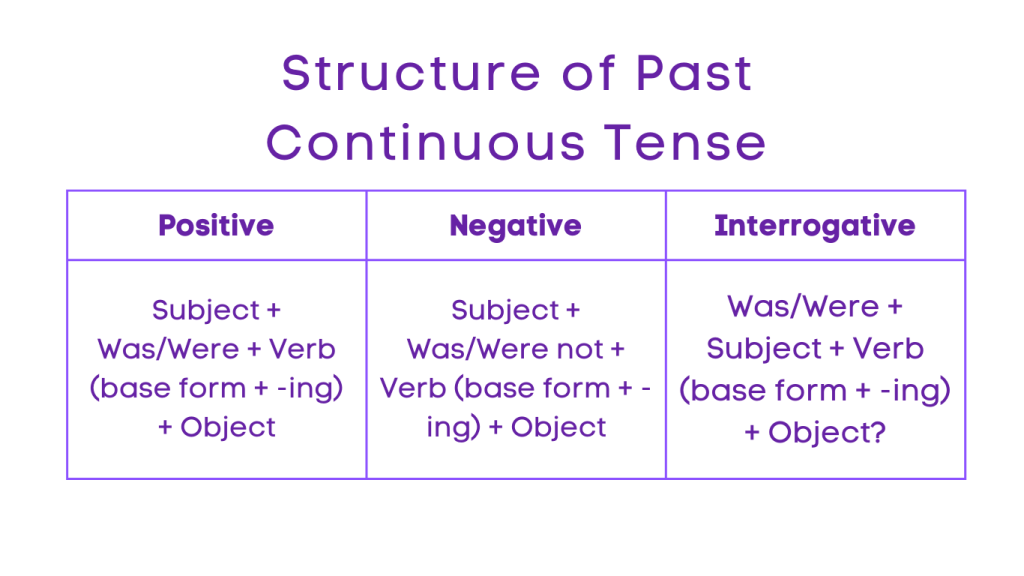
The past continuous tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing or in progress at a specific time in the past. It is formed by using the past form of “to be” (was/were) and the present participle form of the main verb (-ing form).
Structure:
Positive: Subject + Was/Were + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object
Negative: Subject + Was/Were not + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object
Interrogative: Was/Were + Subject + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object?
Negative Interrogative: Was/Were not + Subject + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object?
Past Perfect Tense
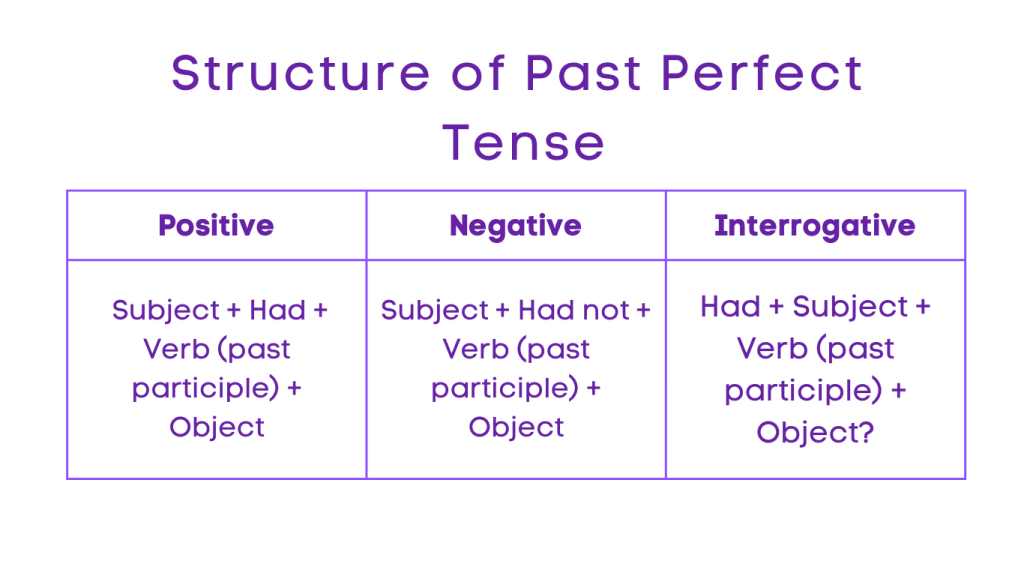
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action that took place before another action in the past. It is formed by using “had” and the past participle form of the main verb.
Structure:
Positive: Subject + Had + Verb (past participle) + Object
Negative: Subject + Had not + Verb (past participle) + Object
Interrogative: Had + Subject + Verb (past participle) + Object?
Negative Interrogative: Had not + Subject + Verb (past participle) + Object?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
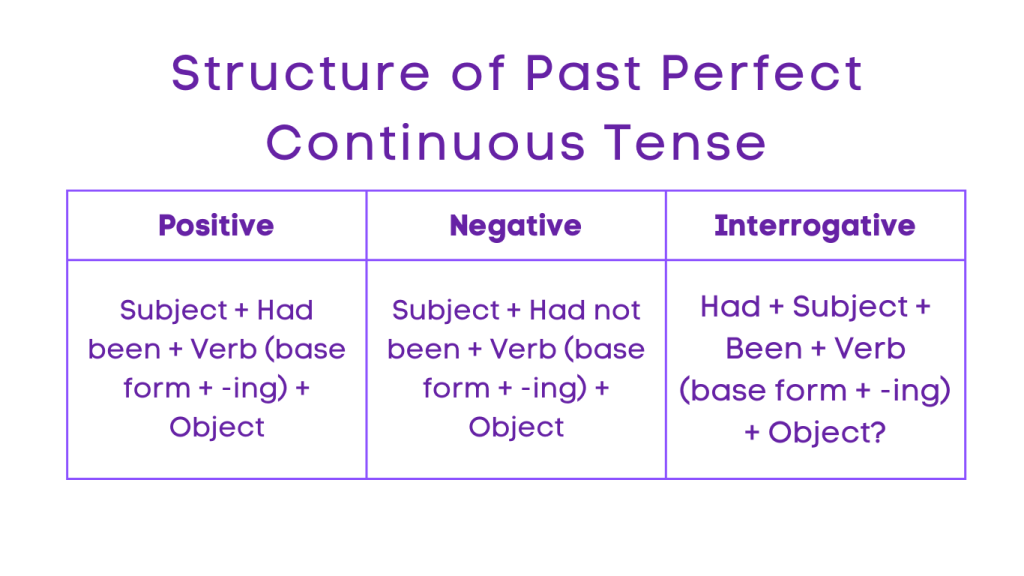
The past perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing or in progress over a period of time before another action in the past. It is formed by using “had been” and the present participle form of the main verb (-ing form).
Structure:
Positive: Subject + Had been + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object
Negative: Subject + Had not been + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object
Interrogative: Had + Subject + Been + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object?
Negative Interrogative: Had not + Subject + Been + Verb (base form + -ing) + Object?
Examples
List of Past Forms
The past forms of regular verbs are created by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. For example:
Walk (base form) – Walked (past form)
Play (base form) – Played (past form)
Jump (base form) – Jumped (past form)
Irregular verbs have specific past forms that do not follow the regular “-ed” pattern. For example:
Go (base form) – Went (past form)
Eat (base form) – Ate (past form)
Sing (base form) – Sang (past form)
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Regular Verbs
Tip: For regular verbs, simply add “-ed” to the base form to form the past tense. For example, “walk” becomes “walked.”
2. Irregular verbs
Tip: Memorize the irregular past tense forms of common verbs, as they don’t follow a consistent pattern. For example, “go” becomes “went,” “eat” becomes “ate,” and “drink” becomes “drank.”
3. Pay attention to spelling changes
Tip: Some verbs undergo spelling changes in the past tense. For example, “study” becomes “studied,” with a change in the final “y” to “i.”
4. Use time markers
Tip: Utilize time markers such as “yesterday,” “last week,” or specific dates to indicate actions that occurred in the past.
5. Practice
Tip: Regular practice and exposure to past tense forms in reading, writing, and speaking will help reinforce your understanding and usage of past tense in English.
Real life application
Story: “A Day in the Past”
In a quaint town, Sarah reminisced about a day filled with past tense experiences that shaped her memories.
Experience 1: The Simple Past
Sarah recalled a trip to the beach where she built sandcastles and collected seashells. She played in the waves and watched the sunset.
Experience 2: The Past Continuous
During the beach trip, Sarah was swimming in the ocean when she saw a dolphin jumping in the distance. She was enjoying the moment when her friends called her to join them for a beach volleyball game.
Experience 3: The Past Perfect
Before the beach trip, Sarah had planned the entire day’s itinerary. She had packed a picnic basket and had prepared snacks for the journey.
Experience 4: The Past Perfect Continuous
Throughout the day, Sarah had been capturing photos of the scenic views and had been recording videos of the fun activities.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends






