Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives
Introduction
Exploring Verbals
In the realm of grammar, verbals play a crucial role in conveying the action and function of words within sentences. Among the various types of verbals, gerunds, participles, and infinitives are essential components that add depth and complexity to the English language. Let’s delve into the world of verbals and unravel the intricacies of gerunds, participles, and infinitives.
Analogy of Definition
What are Verbals?
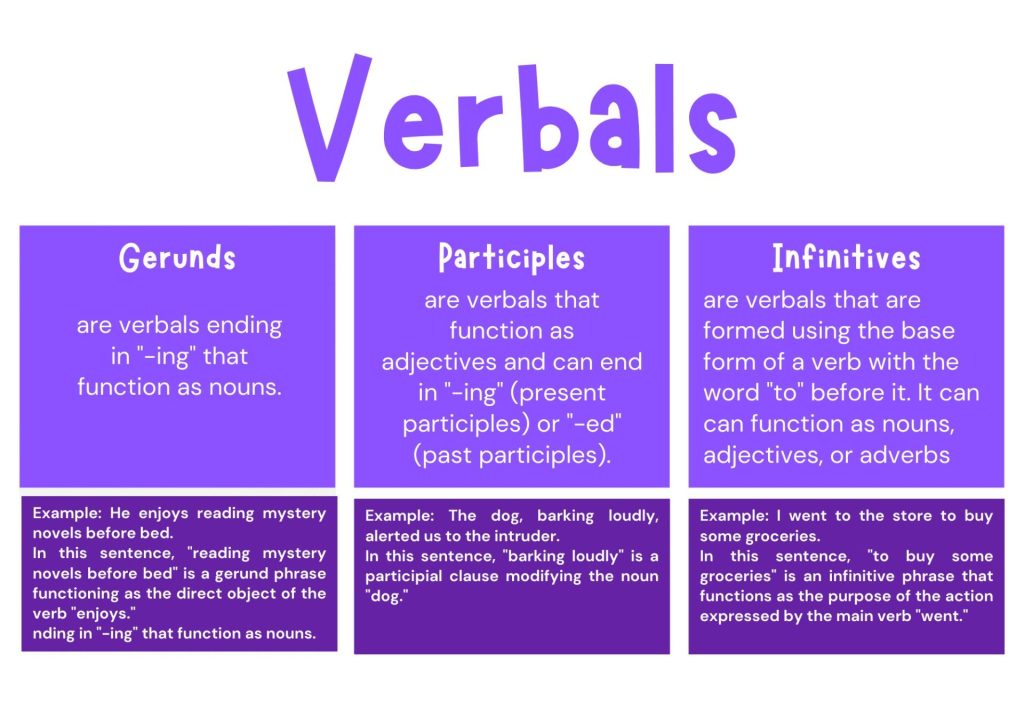
Verbals are words that are formed from verbs but function as different parts of speech within a sentence. Gerunds are verb forms that function as nouns, participles are verb forms that function as adjectives, and infinitives are the base form of a verb with the word “to” that can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs.
Method
Identifying Verbals – Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives
Gerunds are formed by adding “-ing” to a verb and function as nouns.
For example: “swimming” in “Swimming is my favorite activity”, acts as a noun.
Participles are formed by adding “-ing” or “-ed” to a verb and function as adjectives.
For example: “running” in “The running water is refreshing” or “baked” in “The baked cookies are delicious” act as adjectives.
Infinitives are formed with the word “to” followed by a verb and can function as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, such as “to run” in “I love to run.”
Examples
Examples of Verbals
Gerund phrase:
- Example: Eating ice cream on a hot day is refreshing.
- In this sentence, “eating ice cream on a hot day” is a gerund phrase, functioning as the subject of the sentence.
Participle phrase:
- Example: Driven by passion, he pursued his dreams relentlessly.
- In this sentence, “driven by passion” is a participial phrase, modifying the subject “he.”
Infinitive phrase:
- Example: She went to the store to buy some groceries.
- In this sentence, “to buy some groceries” is an infinitive phrase, functioning as the purpose of the action expressed by the main verb “went.”
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1. Using Gerunds as Nouns
Tip: Gerunds function as nouns and can be used as subjects, objects, or complements in a sentence.
Example: Singing (subject) brings me joy.
2. Identifying Participles as Adjectives
Tip: Participles function as adjectives and modify nouns in a sentence.
Example: The fallen (adjective) leaves covered the ground.
3. Understanding Infinitives as Verb Phrases
Tip: Infinitives can function as verb phrases and are often used with auxiliary verbs to convey various meanings.
Example: She wants (verb phrase) to travel the world.
4. Using Gerunds and Infinitives as Objects
Tip: Gerunds and infinitives can function as objects of verbs, prepositions, or adjectives in a sentence.
Example: They decided (object of verb) to go camping.
5. Differentiating Participles and Gerunds
Tip: Participles and gerunds can sometimes look similar, but it’s important to identify their functions within a sentence.
Example: The running (participle) dog chased the ball.
Real life application
Story: “The Adventures of Verbals”
In everyday life, verbals play a significant role in communication, expression, and understanding. Let’s explore how gerunds, participles, and infinitives manifest in real-life scenarios.
Scenario 1: The Art of Cooking
In the culinary world, the use of gerunds, participles, and infinitives is prevalent. Chefs often describe their dishes using participles as adjectives, such as “baked salmon” or “sizzling steak.” Additionally, the act of cooking itself can be expressed using gerunds, as in “Cooking is a form of creative expression.”
Scenario 2: The World of Sports
Athletes and sports enthusiasts frequently use infinitives to express their goals and aspirations. Phrases like “to win the championship” or “to achieve greatness” highlight the use of infinitives as nouns in expressing desires and objectives.
Scenario 3: The Power of Music
In the realm of music, gerunds are commonly used to describe activities related to musical expression. Phrases like “singing in harmony” or “dancing to the rhythm” showcase the use of gerunds as nouns that convey the joy and passion associated with musical endeavors.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends






