What are Adverbs? – Meaning and Examples
Table of Contents
Introduction
Adverbs
Adverbs are an essential part of the English language, adding depth and detail to our communication. Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs, providing information about time, place, manner, degree, frequency, reason, and more. It is one of the eight parts of speech. In this article, we will delve into the various types of adverbs, their usage, and their significance in language.
Analogy of Definition
What are Adverbs?
An adverb is like a spotlight in a sentence, shining its beam on a verb, an adjective, or another adverb to provide more information about how, when, where, or to what extent something happens. Just as a spotlight illuminates and adds clarity to a stage performance, an adverb clarifies and enhances the meaning of a sentence by answering questions like how, when, where, or to what degree an action is performed.
Method
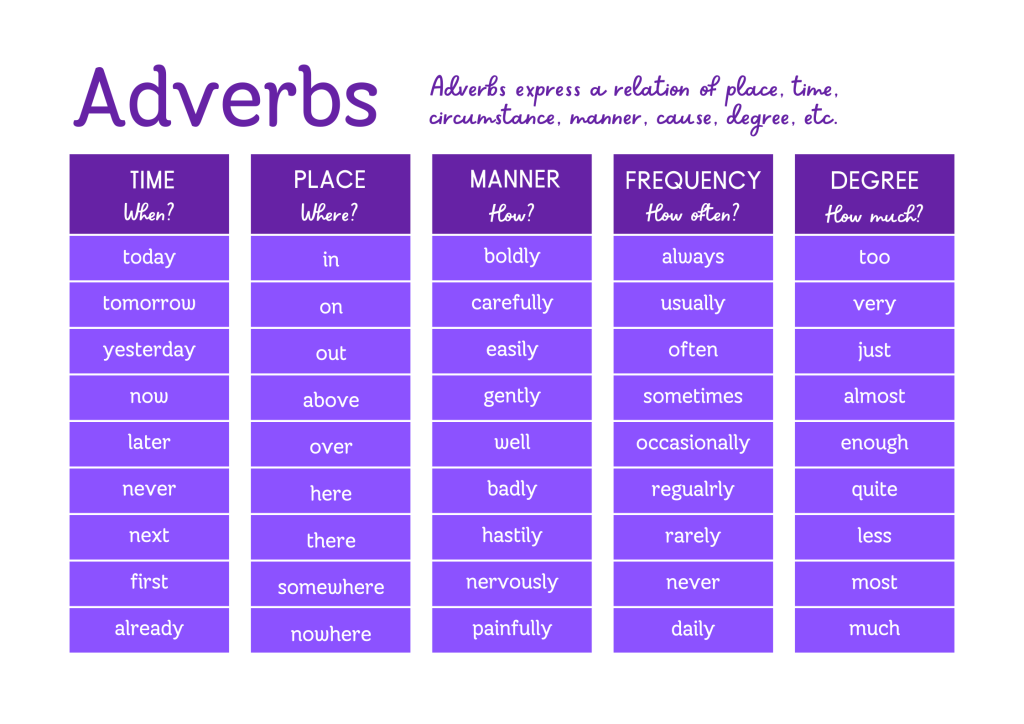
Types of Adverbs
Adverbs can be categorized into different types based on the kind of information they provide. The main types of adverbs include adverbs of time, place, manner, degree, frequency, reason, and conjunctive adverbs. Each type serves a specific purpose in conveying the nuances of language.
Adverb of Time
Adverbs of time indicate when an action takes place. They answer the question “When?” and provide information about the timing or duration of an action. Examples of adverbs of time include “now,” “later,” “soon,” “yesterday,” “today,” “tomorrow,” “always,” “never,” and “often.”
Adverb of Place
Adverbs of place describe the location or position of an action. They answer the question “Where?” and provide details about the spatial aspect of an action. Examples of adverbs of place include “here,” “there,” “everywhere,” “somewhere,” “anywhere,” “upstairs,” “downstairs,” and “abroad.”
Adverb of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. They answer the question “How?” and provide details about the way in which an action is carried out. Examples of adverbs of manner include “quickly,” “slowly,” “carefully,” “elegantly,” “happily,” “sadly,” “well,” and “badly.”
Adverb of Degree
Adverbs of degree indicate the intensity or extent of an action, adjective, or another adverb. They answer the question “To what extent?” and provide information about the degree of a particular quality. Examples of adverbs of degree include “very,” “extremely,” “quite,” “too,” “enough,” “almost,” “entirely,” and “completely.”
Adverb of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency describe how often an action occurs. They answer the question “How often?” and provide details about the regularity or repetition of an action. Examples of adverbs of frequency include “always,” “often,” “sometimes,” “rarely,” “never,” “frequently,” “occasionally,” and “seldom.”
Adverb of Reason
Adverbs of reason explain why an action is performed. They answer the question “Why?” and provide information about the cause or purpose behind an action. Examples of adverbs of reason include “therefore,” “consequently,” “thus,” “hence,” “accordingly,” “so,” and “because.”
Conjunctive Adverb
Conjunctive adverbs connect independent clauses or sentences and show the relationship between ideas. They are used to express transitions, comparisons, contrasts, cause and effect, and other logical relationships. Examples of conjunctive adverbs include “however,” “therefore,” “moreover,” “nevertheless,” “consequently,” “furthermore,” and “meanwhile.”
Adverb vs Verb
It is important to differentiate between adverbs and verbs, as they serve distinct functions in a sentence. While verbs express actions or states of being, adverbs modify or describe those actions or states. For example, in the sentence “She sings beautifully,” “sings” is the verb, and “beautifully” is the adverb modifying the action.
Adverb vs Adjective
Adverbs and adjectives are closely related, but they serve different purposes in a sentence. Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, while adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. For example, in the sentence “He runs quickly,” “quickly” is an adverb modifying the verb “runs,” whereas in the sentence “She is extremely talented,” “extremely” is an adverb modifying the adjective “talented.”
How to Use Adverbs
To use adverbs effectively, it is important to understand their placement and function in a sentence. Adverbs can appear before or after the verb they modify, as well as before adjectives or other adverbs. They can also be used to modify an entire sentence. It is essential to choose the appropriate adverb based on the context and the type of information being conveyed.
Examples
1. Adverbs of Time: now, later, soon, yesterday, today, tomorrow, always, never, often
2. Adverbs of Place: here, there, everywhere, somewhere, anywhere, upstairs, downstairs, abroad
3. Adverbs of Manner: quickly, slowly, carefully, elegantly, happily, sadly, well, badly
4. Adverbs of Degree: very, extremely, quite, too, enough, almost, entirely, completely
5. Adverbs of Frequency: always, often, sometimes, rarely, never, frequently, occasionally, seldom
6. Adverbs of Reason: therefore, consequently, thus, hence, accordingly, so, because
7. Conjunctive Adverbs: however, therefore, moreover, nevertheless, consequently, furthermore, meanwhile
Quiz
Tips and Tricks
1.Identify the Adverb’s Role
Tip: Understand that adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs in a sentence. They provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is performed.
2.Spotting Adverbs
Tip: Look for words that typically end in “-ly,” such as quickly, slowly, happily, or angrily. While not all adverbs end in “-ly,” many do, making it a helpful clue when identifying them in a sentence.
3.Watch for Exceptions
Tip: Be aware that not all adverbs end in “-ly.” Some common adverbs, like “soon,” “now,” and “very,” do not follow this pattern. Recognizing these exceptions can help you identify adverbs more accurately.
4.Use Adverbs Properly
Tip: While adverbs can add detail and clarity to a sentence, using them excessively can make writing feel cluttered and weaken the impact of your message. Aim for precision and choose adverbs that enhance the meaning without overloading the sentence.
5.Positioning Matters
Tip: Pay attention to where adverbs are placed in a sentence. Adverbs can be positioned before the verb, after the verb, or at the beginning or end of a sentence for emphasis. Understanding the placement rules can help you use adverbs effectively.
Real life application
Story: “The Adverb Adventures of Emma and Max”
Emma and Max were two curious explorers who embarked on a journey to uncover the significance of adverbs in everyday life. As they ventured through different scenarios, they encountered real-life applications of adverbs that showcased their practical relevance.
Scenario 1: The Time Management Challenge
Emma and Max were tasked with organizing a series of events for a community festival. They had to schedule performances, workshops, and activities at specific times. Adverbs of time helped them plan the sequence of events and ensure that everything ran smoothly.
Scenario 2: The Travel Planning Quest
As they prepared for a road trip, Emma and Max used adverbs of place to navigate their route and locate various landmarks and attractions. Adverbs of place provided them with directions and descriptions of different locations, making their travel experience more enjoyable.
Scenario 3: The Cooking Competition Dilemma
In a cooking competition, Emma and Max had to prepare dishes with specific instructions. Adverbs of manner guided them in executing cooking techniques and flavor combinations, allowing them to create delicious and well-presented meals.
Scenario 4: The Academic Achievement Challenge
Emma and Max utilized adverbs of degree to express the level of their academic performance and achievements. Adverbs of degree helped them communicate the extent of their knowledge, skills, and accomplishments in various subjects and activities.
Scenario 5: The Health and Wellness Journey
In their pursuit of a healthy lifestyle, Emma and Max incorporated adverbs of frequency into their daily routines. Adverbs of frequency enabled them to establish consistent habits and track their progress in maintaining a balanced and active lifestyle.
FAQ's
Like? Share it with your friends
